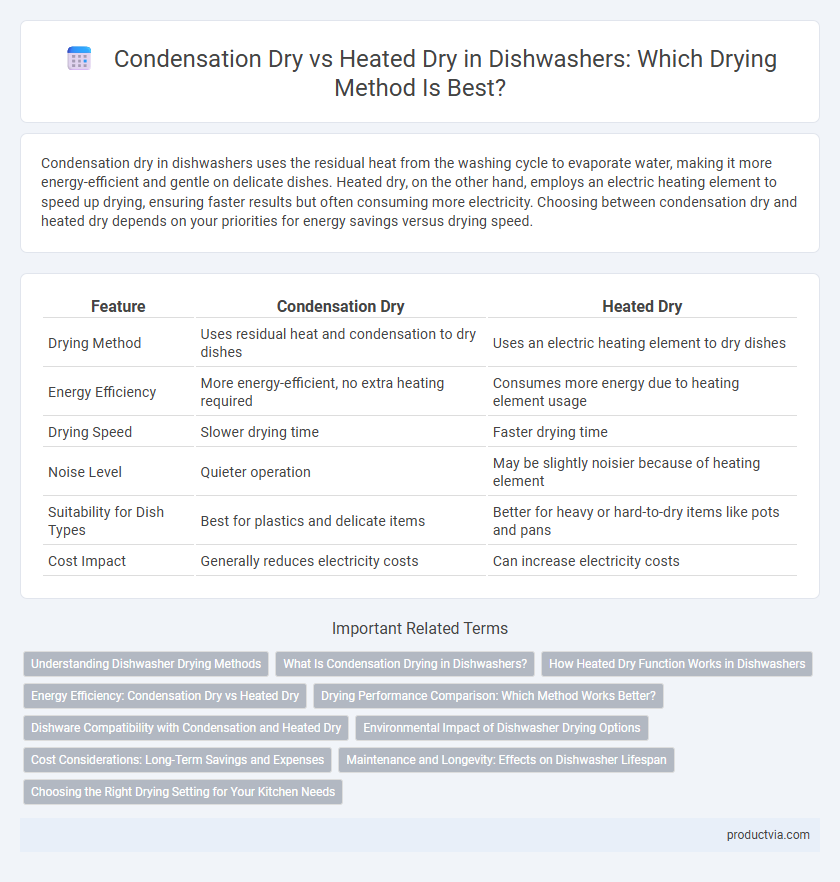
Condensation dry in dishwashers uses the residual heat from the washing cycle to evaporate water, making it more energy-efficient and gentle on delicate dishes. Heated dry, on the other hand, employs an electric heating element to speed up drying, ensuring faster results but often consuming more electricity. Choosing between condensation dry and heated dry depends on your priorities for energy savings versus drying speed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Condensation Dry | Heated Dry |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Uses residual heat and condensation to dry dishes | Uses an electric heating element to dry dishes |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient, no extra heating required | Consumes more energy due to heating element usage |
| Drying Speed | Slower drying time | Faster drying time |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | May be slightly noisier because of heating element |
| Suitability for Dish Types | Best for plastics and delicate items | Better for heavy or hard-to-dry items like pots and pans |
| Cost Impact | Generally reduces electricity costs | Can increase electricity costs |
Understanding Dishwasher Drying Methods
Condensation dry uses the residual heat from the dishwasher's final rinse cycle to evaporate water, allowing moisture to condense on the cooler stainless steel tub walls and drain away, making it energy-efficient and quieter. Heated dry employs an electric heating element to actively warm the interior, speeding up drying time but increasing energy consumption and sometimes causing slight warping on plastic items. Understanding these methods helps consumers choose between energy savings with condensation drying and quicker, more thorough drying with heated options.
What Is Condensation Drying in Dishwashers?
Condensation drying in dishwashers uses the natural cooling process to remove moisture from dishes by allowing hot, moist air to condense on the cooler stainless steel walls of the dishwasher. This method is energy-efficient and eco-friendly, as it avoids the use of heating elements to dry dishes. It is ideal for plastics and delicate items that may warp or melt with heated drying.
How Heated Dry Function Works in Dishwashers
The heated dry function in dishwashers uses an electric heating element to raise the temperature inside the dishwasher, effectively evaporating water from dishes for faster drying. This process ensures a more thorough and quicker drying cycle compared to condensation drying, which relies on residual heat and air circulation to evaporate moisture. Heated drying consumes more energy but delivers consistently drier results, especially for plastic items that are harder to dry with condensation methods.
Energy Efficiency: Condensation Dry vs Heated Dry
Condensation dry uses the heat from the washing cycle to evaporate moisture, consuming less energy than heated dry, which relies on an electric heating element to actively dry dishes. Energy-efficient dishwashers often feature condensation drying as it reduces electricity usage while maintaining effective drying performance. Choosing a model with condensation dry can lower utility costs and decrease the environmental impact compared to heated dry options.
Drying Performance Comparison: Which Method Works Better?
Condensation dry in dishwashers uses natural evaporation by releasing steam and relying on cooler surfaces inside the unit, resulting in energy-efficient but sometimes less effective drying, especially for plastic items. Heated dry employs electric heating elements to actively warm the interior, accelerating moisture evaporation and providing consistently drier dishes but with higher energy consumption. Studies and user reviews indicate heated dry offers superior drying performance across diverse dish types, whereas condensation dry excels in eco-friendliness and cost savings.
Dishware Compatibility with Condensation and Heated Dry
Condensation dry uses lower temperatures and natural air circulation, making it gentler on delicate dishware such as plastic, glass, and non-stick surfaces, reducing the risk of warping or damage. Heated dry employs a heating element that raises the temperature to speed up drying, which can cause melting or warping in heat-sensitive items but provides faster results for heavy or thick items like ceramic or metal cookware. Understanding dishware compatibility ensures optimal drying performance while preserving the integrity of various materials in your dishwasher.
Environmental Impact of Dishwasher Drying Options
Condensation dry cycle uses residual heat and ambient air, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to heated dry options, which rely on electric heating elements that increase electricity usage and carbon footprint. Choosing condensation drying can lower greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing power demand, promoting a more sustainable kitchen appliance operation. Environmentally conscious consumers benefit from condensation dry settings by reducing overall household energy usage and associated environmental impact.
Cost Considerations: Long-Term Savings and Expenses
Condensation dry systems in dishwashers typically use less energy because they rely on natural evaporation, resulting in lower electricity bills over time compared to heated dry options that consume more power by actively warming the air. While heated dry cycles can shorten drying duration and improve convenience, their higher energy consumption often leads to increased operational costs, impacting long-term savings. Choosing condensation dry technology offers a cost-effective solution by minimizing energy expenses without sacrificing drying performance, making it ideal for budget-conscious consumers.
Maintenance and Longevity: Effects on Dishwasher Lifespan
Condensation dry cycles use residual heat and cool air to evaporate moisture, reducing wear on heating elements and extending dishwasher lifespan by minimizing component stress. Heated dry cycles rely on electrical heating elements to speed up drying, which can increase energy consumption and accelerate wear on parts, potentially decreasing the machine's longevity. Choosing condensation drying promotes maintenance efficiency and supports long-term durability by limiting heat exposure to dishwasher components.
Choosing the Right Drying Setting for Your Kitchen Needs
Condensation dry uses residual heat and natural moisture evaporation, making it energy-efficient and ideal for plastic dishes or delicate items. Heated dry employs an electric heating element to speed up drying, perfect for heavier cookware or faster kitchen turnaround. Selecting the right drying setting enhances energy savings, prevents damage to dishware, and optimizes your dishwasher's performance based on your daily usage.
Condensation Dry vs Heated Dry for Dishwashers Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com