Condensation drying in dishwashers relies on the natural evaporation of water, using cooler interior walls to condense steam and eliminate moisture without extra energy consumption. Heated drying involves electric elements that actively warm the dishwasher's interior, accelerating drying but increasing energy usage. Choosing condensation drying enhances energy efficiency and reduces utility costs, while heated drying offers faster results for those needing quick dish readiness.
Table of Comparison
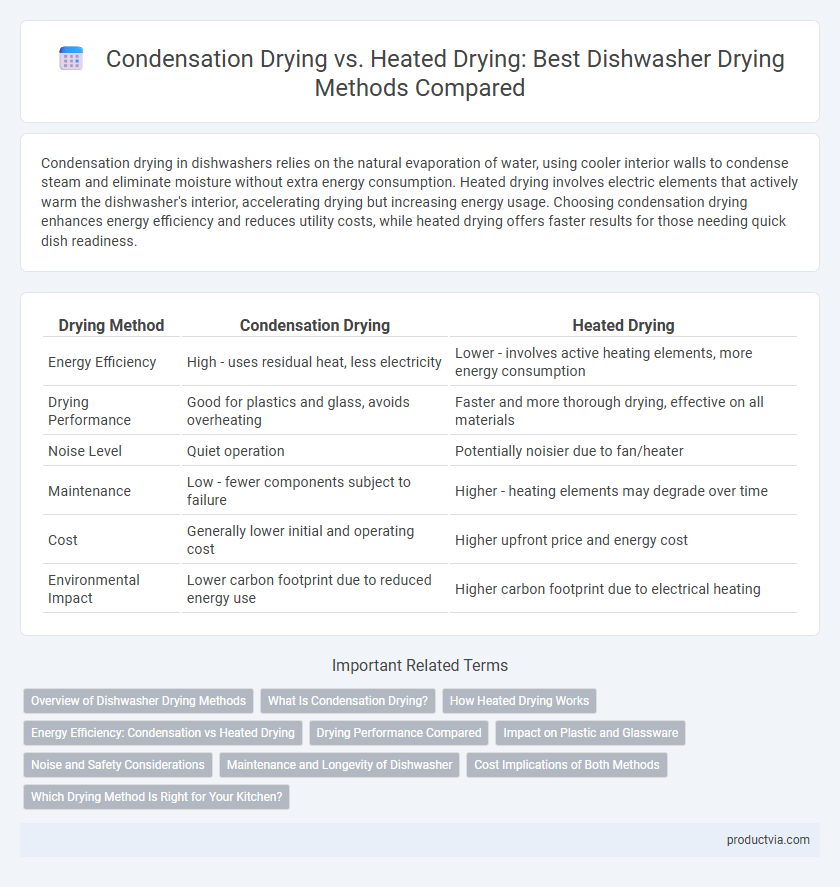
| Drying Method | Condensation Drying | Heated Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High - uses residual heat, less electricity | Lower - involves active heating elements, more energy consumption |
| Drying Performance | Good for plastics and glass, avoids overheating | Faster and more thorough drying, effective on all materials |
| Noise Level | Quiet operation | Potentially noisier due to fan/heater |
| Maintenance | Low - fewer components subject to failure | Higher - heating elements may degrade over time |
| Cost | Generally lower initial and operating cost | Higher upfront price and energy cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to reduced energy use | Higher carbon footprint due to electrical heating |
Overview of Dishwasher Drying Methods
Condensation drying in dishwashers utilizes remaining heat and moisture absorption to evaporate water without extra energy, making it an energy-efficient option. Heated drying employs an internal heating element to increase temperature and accelerate water evaporation, resulting in faster drying but higher energy consumption. Both methods impact drying performance, energy use, and noise levels, with condensation drying favored for eco-friendly models and heated drying common in high-performance dishwashers.
What Is Condensation Drying?
Condensation drying in dishwashers relies on the natural process of heat transfer, where steam generated during the final rinse condenses on the cooler stainless steel walls, turning into water that drains away. This energy-efficient method eliminates the need for a heating element, reducing electricity consumption and preventing plastic items from melting. Unlike heated drying systems that use electric heaters to blow warm air, condensation drying is quieter and gentler on dishes while maintaining effective drying performance.
How Heated Drying Works
Heated drying in dishwashers uses an electric heating element to raise the temperature inside the dishwasher, accelerating the evaporation of water from dishes. This method ensures faster and more thorough drying by converting moisture into steam, which is then vented out of the appliance. Heated drying typically results in drier dishes compared to condensation drying, which relies on cooling and natural condensation to remove moisture.
Energy Efficiency: Condensation vs Heated Drying
Condensation drying in dishwashers uses residual heat to evaporate water, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to heated drying methods that rely on electric heating elements. Energy-efficient condensation drying lowers electricity usage by approximately 10-15%, contributing to reduced utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Modern dishwashers with condensation drying cycles typically achieve better Energy Star ratings than those using heated drying, making them more eco-friendly options.
Drying Performance Compared
Condensation drying in dishwashers relies on natural evaporation and typically results in less energy consumption but can leave plastic items slightly damp. Heated drying uses an electric heating element to boost drying temperatures, improving drying performance and ensuring dishes, including plastics, come out fully dry. Studies demonstrate heated drying achieves a higher moisture reduction rate, enhancing convenience but increasing energy usage compared to condensation drying.
Impact on Plastic and Glassware
Condensation drying in dishwashers uses residual heat to evaporate moisture, preserving the integrity of plastic items by preventing warping and reducing spots on glassware caused by high heat. Heated drying employs electric heating elements to speed up drying but can cause plastic to deform and increase the risk of cloudiness or etching on glass surfaces over time. Choosing condensation drying enhances the longevity of plastic utensils and maintains the clarity of delicate glassware.
Noise and Safety Considerations
Condensation drying in dishwashers operates quietly by using residual heat and cool air circulation, minimizing noise levels compared to heated drying methods that rely on noisy heating elements. Safety considerations favor condensation drying due to lower operating temperatures, reducing risks of burns or heat-related malfunctions, whereas heated drying can pose higher safety concerns from hot surfaces. Choosing condensation drying enhances overall user safety and offers a quieter kitchen environment.
Maintenance and Longevity of Dishwasher
Condensation drying in dishwashers reduces wear on heating elements and prevents the buildup of mineral deposits, enhancing the longevity of internal components. Heated drying, although faster, exposes heating elements to constant thermal stress, potentially accelerating component wear and requiring more frequent maintenance. Choosing condensation drying supports sustained dishwasher performance and lowers the risk of costly repairs over time.
Cost Implications of Both Methods
Condensation drying in dishwashers typically consumes less energy than heated drying, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced operational costs. Heated drying methods use electric heating elements that increase energy usage, leading to higher long-term expenses despite faster drying times. Choosing condensation drying can provide significant cost savings over time by minimizing energy consumption without compromising drying performance.
Which Drying Method Is Right for Your Kitchen?
Condensation drying in dishwashers uses natural steam condensation to cool dishes, making it energy-efficient and quieter, ideal for environmentally conscious kitchens. Heated drying employs electric heating elements to speed up the drying process, providing faster and more thorough results, perfect for busy households needing quick dish turnaround. Choosing between condensation drying and heated drying depends on your priorities for energy savings, noise level, and drying speed in your kitchen.
Condensation drying vs Heated drying for dishwasher drying methods Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com