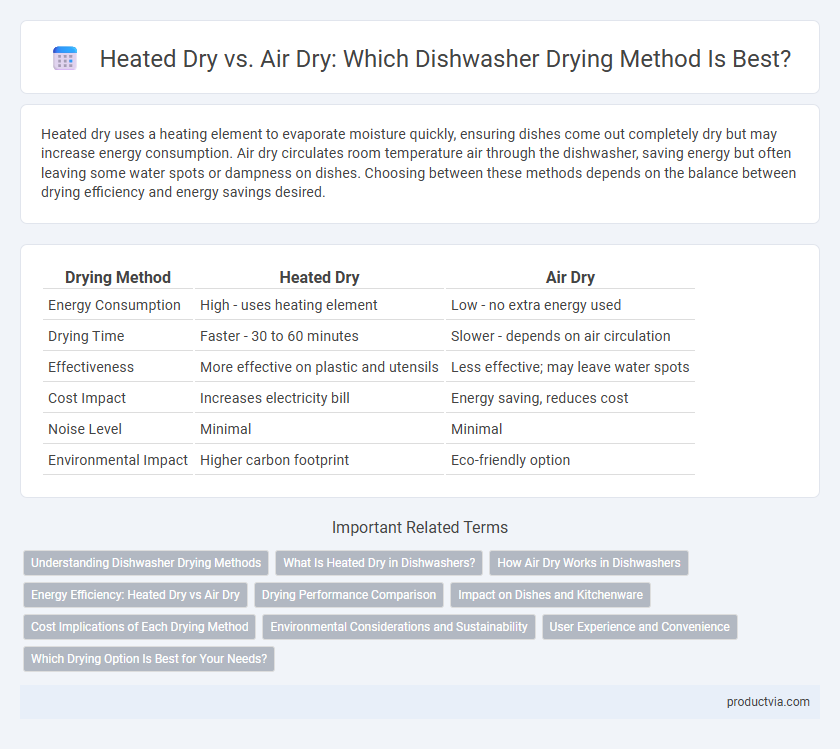
Heated dry uses a heating element to evaporate moisture quickly, ensuring dishes come out completely dry but may increase energy consumption. Air dry circulates room temperature air through the dishwasher, saving energy but often leaving some water spots or dampness on dishes. Choosing between these methods depends on the balance between drying efficiency and energy savings desired.
Table of Comparison
| Drying Method | Heated Dry | Air Dry |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | High - uses heating element | Low - no extra energy used |
| Drying Time | Faster - 30 to 60 minutes | Slower - depends on air circulation |
| Effectiveness | More effective on plastic and utensils | Less effective; may leave water spots |
| Cost Impact | Increases electricity bill | Energy saving, reduces cost |
| Noise Level | Minimal | Minimal |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Eco-friendly option |
Understanding Dishwasher Drying Methods
Heated dry uses an internal heating element to evaporate moisture from dishes, ensuring faster and more thorough drying. Air dry relies on natural air circulation without added heat, making it more energy-efficient but sometimes leaving water spots. Choosing the right drying method depends on balancing energy consumption, drying effectiveness, and dish safety.
What Is Heated Dry in Dishwashers?
Heated dry in dishwashers uses an electric heating element to raise the temperature inside the appliance, accelerating the evaporation of water from dishes and ensuring a thorough drying process. This method is especially effective for cutting through moisture on plastic and heavier items that resist air drying. Although it consumes more energy than air dry, heated drying delivers faster, more consistent, and streak-free results.
How Air Dry Works in Dishwashers
Air dry in dishwashers uses the natural circulation of air to evaporate moisture from dishes at the end of the wash cycle, minimizing energy consumption compared to heated dry. This method often involves opening the dishwasher door slightly after the cycle to allow humid air to escape and cooler air to enter, enhancing the evaporation process. Air dry reduces the risk of heat damage to delicate items and lowers electricity usage while maintaining effective drying performance.
Energy Efficiency: Heated Dry vs Air Dry
Heated dry uses an electric heating element to evaporate water, consuming significantly more energy compared to air dry, which relies on natural convection and moisture release from dishes. Air dry reduces electricity consumption by eliminating the warming process, making it a more energy-efficient drying method. Choosing air dry can lower household energy bills and reduce environmental impact while maintaining effective drying performance.
Drying Performance Comparison
Heated dry uses high temperatures to evaporate water quickly, ensuring dishes come out completely dry and streak-free, especially effective for plastic and glassware. Air dry relies on natural airflow and residual heat, consuming less energy but often leaving moisture on dishes, particularly in humid environments. Heated dry offers superior drying performance with consistent results, while air dry provides an energy-efficient alternative with occasional dampness.
Impact on Dishes and Kitchenware
Heated dry in dishwashers uses a heating element to evaporate water quickly, which can cause warping or damage to delicate plastics and increase energy consumption. Air dry relies on natural ventilation or a fan, preserving the integrity of sensitive kitchenware while being more energy-efficient but often leaving some residual moisture. Choosing between heated dry and air dry significantly affects the longevity of dishes, especially plastic and non-stick items, and influences overall energy usage in the kitchen.
Cost Implications of Each Drying Method
Heated dry cycles in dishwashers consume more electricity, increasing energy costs compared to air dry methods that rely on natural evaporation without added power. Air dry is more cost-effective, reducing utility bills by eliminating the heating element's energy usage. Choosing air dry extends appliance savings, while heated dry offers faster results at a higher operating expense.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Heated dry uses electricity to blow warm air, increasing energy consumption and carbon emissions, while air dry relies on natural evaporation, significantly reducing environmental impact. Opting for air dry reduces the dishwasher's overall carbon footprint, supporting sustainable energy use and lowering utility bills. Choosing energy-efficient drying methods contributes to long-term resource conservation and aligns with eco-friendly household practices.
User Experience and Convenience
Heated dry in dishwashers delivers faster, more effective drying by applying consistent warmth to evaporate water quickly, reducing the need for manual towel drying. Air dry uses natural airflow for energy efficiency but often leaves dishes damp, requiring additional drying time or hand drying. Users seeking convenience and spotless results typically prefer heated dry for its reliable performance and time-saving benefits.
Which Drying Option Is Best for Your Needs?
Heated dry in dishwashers uses built-in heating elements to efficiently evaporate water, ensuring dishes come out completely dry but consuming more energy. Air dry relies on natural airflow and condensation, offering an energy-saving alternative ideal for plastic items that may warp under heat. Choose heated dry for spotless, quick results or air dry to prioritize energy efficiency and gentler drying for delicate dishware.
Heated Dry vs Air Dry for Drying Method Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com