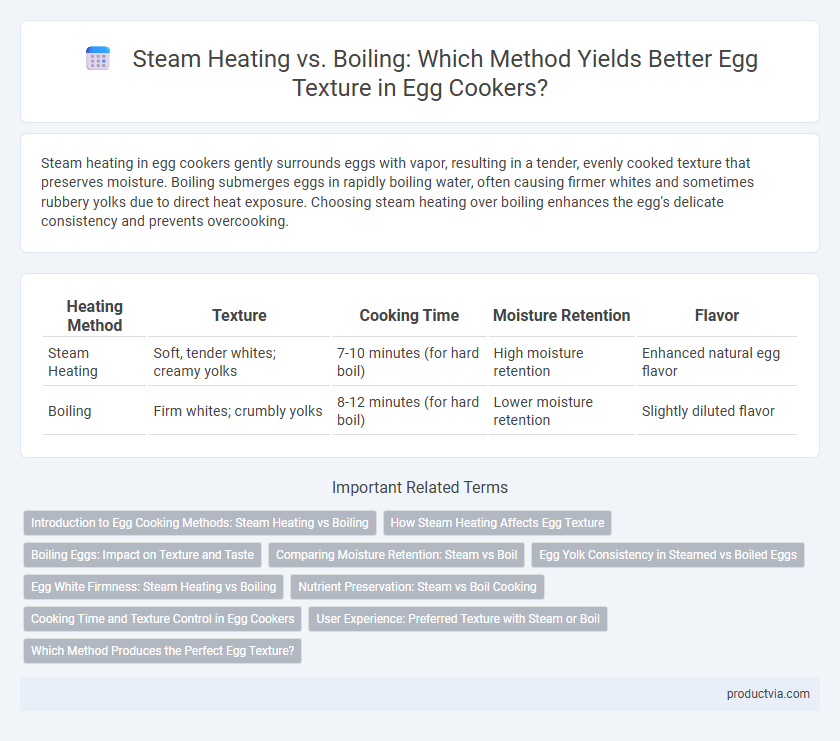
Steam heating in egg cookers gently surrounds eggs with vapor, resulting in a tender, evenly cooked texture that preserves moisture. Boiling submerges eggs in rapidly boiling water, often causing firmer whites and sometimes rubbery yolks due to direct heat exposure. Choosing steam heating over boiling enhances the egg's delicate consistency and prevents overcooking.
Table of Comparison
| Heating Method | Texture | Cooking Time | Moisture Retention | Flavor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Heating | Soft, tender whites; creamy yolks | 7-10 minutes (for hard boil) | High moisture retention | Enhanced natural egg flavor |
| Boiling | Firm whites; crumbly yolks | 8-12 minutes (for hard boil) | Lower moisture retention | Slightly diluted flavor |
Introduction to Egg Cooking Methods: Steam Heating vs Boiling
Steam heating preserves the egg's moisture and produces a tender, evenly cooked texture, preventing overcooking and rubberiness common in boiling. Boiling immerses eggs in water at high temperatures, often leading to firmer whites and a chalky yolk if cooked too long. Understanding these differences allows for precise control over egg texture in various cooking preferences.
How Steam Heating Affects Egg Texture
Steam heating preserves the egg's delicate proteins by cooking more evenly and gently compared to boiling, resulting in a creamier, softer yolk and tender whites. The consistent moisture and lower temperature from steam minimize the risk of overcooking and rubbery textures often caused by direct boiling. This method enhances the egg's natural flavor and smooth texture, making steam heating a preferred choice for ideal egg consistency.
Boiling Eggs: Impact on Texture and Taste
Boiling eggs in water creates a firm, consistent texture by cooking the whites and yolks uniformly through direct heat transfer. The high temperature of boiling water solidifies proteins quickly, resulting in a dense egg white and a creamy to crumbly yolk depending on cooking time. This method enhances the egg's savory flavor while retaining moisture better than dry-heat alternatives, contributing to its characteristic taste and mouthfeel.
Comparing Moisture Retention: Steam vs Boil
Steam heating preserves moisture inside eggs more effectively than boiling, resulting in a tender and moist texture. Boiling submerges eggs in water, leading to greater moisture loss and a firmer, sometimes rubbery consistency. Choosing steam cooking enhances the egg's smoothness and creaminess by minimizing water penetration and preventing overcooking.
Egg Yolk Consistency in Steamed vs Boiled Eggs
Steam heating produces eggs with a creamier, more tender yolk compared to the firmer and drier yolk texture found in boiled eggs. The gentle steam heat allows the yolk to cook evenly and retain moisture, resulting in a custard-like consistency. In contrast, boiling subjects eggs to direct water heat, often causing the yolk to become chalky and less smooth.
Egg White Firmness: Steam Heating vs Boiling
Steam heating produces firmer egg whites compared to boiling due to the gentler, more consistent heat transfer that prevents overcooking. Boiling causes direct water contact, which can lead to rubbery, unevenly cooked egg whites as the proteins coagulate too quickly. For optimal egg white texture, steam heating maintains a tender yet firm consistency, enhancing overall egg quality.
Nutrient Preservation: Steam vs Boil Cooking
Steam heating retains more nutrients in eggs compared to boiling because it exposes eggs to less water, reducing nutrient leaching. The gentle heat from steam preserves delicate vitamins such as B-complex and vitamin A, which are more prone to degradation in boiling water. As a result, steam-cooked eggs maintain a richer nutritional profile and a tender texture, enhancing both health benefits and sensory experience.
Cooking Time and Texture Control in Egg Cookers
Steam heating in egg cookers provides precise temperature control, resulting in evenly cooked eggs with a tender, smooth texture. Boiling often leads to harsher textures due to direct water immersion and fluctuating temperatures, while steam heating reduces overcooking risks and delivers consistent firmness. Cooking time with steam is typically shorter and more predictable, enhancing texture control and overall egg quality.
User Experience: Preferred Texture with Steam or Boil
Steam heating preserves the egg's delicate texture by cooking it evenly without submerging it in water, resulting in a tender and smooth white with a creamy yolk. Boiling often causes the egg white to become firmer and can sometimes lead to rubbery texture due to direct contact with water at high temperatures. Users seeking a consistent, softer, and more flavorful egg frequently prefer steam heating for an enhanced culinary experience.
Which Method Produces the Perfect Egg Texture?
Steam heating produces a more evenly cooked egg with a tender, creamy texture, preventing the rubbery whites and chalky yolks often found in boiling. Boiling submerges eggs in water at a rolling boil, which can lead to overcooked edges and uneven doneness. For consistent results and a perfect balance of firmness and creaminess, steam cooking is the preferred method in egg cookers.
Steam heating vs boiling for egg texture Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com