Pyrolytic oven liners use high temperatures to burn off food residues into ash, which is easy to wipe away, offering a thorough and effective cleaning method. Catalytic liners absorb and break down grease and fats during regular cooking, requiring less intense cleaning but may need replacement over time as their effectiveness diminishes. Choosing between pyrolytic and catalytic liners depends on the convenience of maintenance and the frequency of heavy cooking residues inside the oven.
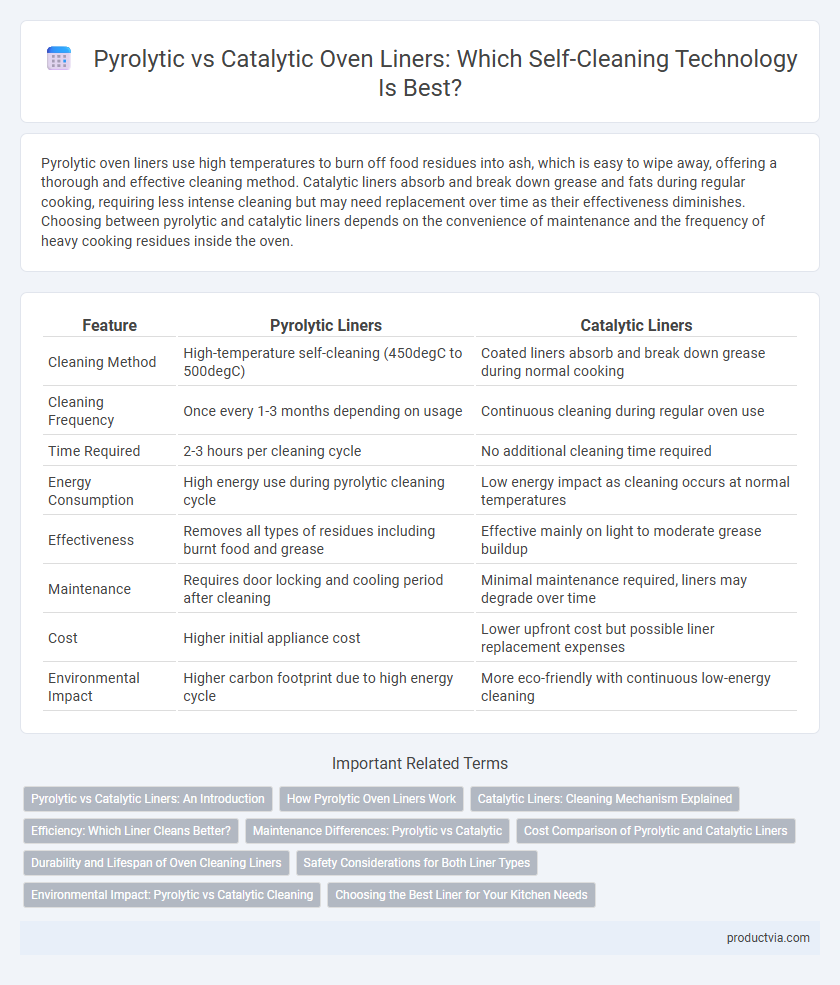
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pyrolytic Liners | Catalytic Liners |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning Method | High-temperature self-cleaning (450degC to 500degC) | Coated liners absorb and break down grease during normal cooking |
| Cleaning Frequency | Once every 1-3 months depending on usage | Continuous cleaning during regular oven use |
| Time Required | 2-3 hours per cleaning cycle | No additional cleaning time required |
| Energy Consumption | High energy use during pyrolytic cleaning cycle | Low energy impact as cleaning occurs at normal temperatures |
| Effectiveness | Removes all types of residues including burnt food and grease | Effective mainly on light to moderate grease buildup |
| Maintenance | Requires door locking and cooling period after cleaning | Minimal maintenance required, liners may degrade over time |
| Cost | Higher initial appliance cost | Lower upfront cost but possible liner replacement expenses |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint due to high energy cycle | More eco-friendly with continuous low-energy cleaning |
Pyrolytic vs Catalytic Liners: An Introduction
Pyrolytic liners use high temperatures up to 500degC to incinerate food residues into ash, making cleaning effortless by simply wiping the cooled surface. Catalytic liners contain a porous coating that absorbs and breaks down grease and food splatters during regular oven use, requiring lower temperatures and less energy for self-cleaning. Choosing between pyrolytic and catalytic liners depends on user preference for intensive high-heat cleaning versus continuous low-temperature maintenance.
How Pyrolytic Oven Liners Work
Pyrolytic oven liners work by utilizing extremely high temperatures, typically around 480degC (900degF), to incinerate food residues and grease into ash, which can then be easily wiped away. These liners are coated with a special heat-resistant glaze that allows the oven to reach and maintain the intense cleaning temperature without damage. This self-cleaning process eliminates the need for chemical cleaning agents, making pyrolytic ovens highly efficient and environmentally friendly.
Catalytic Liners: Cleaning Mechanism Explained
Catalytic liners in ovens clean by breaking down grease and food residues using a special porous enamel coating that absorbs and oxidizes dirt during regular cooking cycles. This self-cleaning process eliminates the need for high-temperature pyrolytic cleaning, reducing energy consumption and odor. The catalytic reaction helps maintain the oven's cleanliness with minimal manual effort, making it an efficient and eco-friendly alternative to traditional cleaning methods.
Efficiency: Which Liner Cleans Better?
Pyrolytic liners clean ovens more efficiently by reaching temperatures up to 500degC, incinerating grease and food residues into ash that can be easily wiped away. Catalytic liners absorb and break down grease during regular cooking at lower temperatures, providing continuous cleaning but often requiring more frequent maintenance. For thorough and fast cleaning, pyrolytic liners deliver superior results, especially in heavily soiled ovens.
Maintenance Differences: Pyrolytic vs Catalytic
Pyrolytic ovens use high temperatures to incinerate food residues, turning them into ash that requires manual removal after each cleaning cycle, which can take one to three hours. Catalytic liners absorb grease and organic dirt during regular cooking at lower temperatures and self-clean during normal oven use, reducing the frequency of maintenance but necessitating replacement every few years. Pyrolytic cleaning demands higher energy consumption and longer downtime compared to the more energy-efficient, ongoing cleaning process of catalytic liners.
Cost Comparison of Pyrolytic and Catalytic Liners
Pyrolytic liners generally have a higher upfront cost compared to catalytic liners due to advanced heat-resistant materials and integrated self-cleaning technology. Catalytic liners are less expensive initially but may incur higher maintenance costs over time as their effectiveness diminishes with wear and requires periodic replacement or manual cleaning. Considering energy consumption, pyrolytic ovens often use more electricity during cleaning cycles, impacting long-term operational expenses.
Durability and Lifespan of Oven Cleaning Liners
Pyrolytic oven cleaning liners offer superior durability and lifespan by withstanding extremely high temperatures during self-cleaning cycles, breaking down grease and food residues into ash without degrading the lining material. Catalytic liners feature porous surfaces that absorb and oxidize grease at lower temperatures but tend to wear out faster, requiring replacement every few years. Choosing pyrolytic liners ensures longer-lasting performance and less frequent maintenance compared to catalytic alternatives.
Safety Considerations for Both Liner Types
Pyrolytic liners use extremely high temperatures to incinerate residue, requiring ovens with advanced heat-resistant materials and safety features to prevent burns or fire hazards. Catalytic liners rely on chemical reactions to break down grease at lower temperatures, reducing the risk of overheating but necessitating careful monitoring to ensure the catalyst remains effective and uncontaminated. Both liner types demand proper ventilation and maintenance to avoid the buildup of toxic fumes or harmful residues during the cleaning cycle.
Environmental Impact: Pyrolytic vs Catalytic Cleaning
Pyrolytic oven liners use extremely high temperatures to burn off grease and food residues, converting them into ash and minimizing chemical use, which reduces environmental pollution. Catalytic liners absorb and break down grease at lower temperatures through a chemical process, leading to energy-efficient cleaning but may involve periodic replacement to maintain efficacy. Pyrolytic cleaning's higher energy consumption contrasts with the catalytic method's potential for lower energy use but requires consideration of waste from spent liners.
Choosing the Best Liner for Your Kitchen Needs
Pyrolytic liners use intense heat to burn off grease and food residue, offering a thorough, high-temperature clean ideal for heavy-duty cooking environments. Catalytic liners absorb and break down grease during regular oven use, providing continuous cleaning with lower energy consumption and less maintenance. Selecting the best liner depends on your cooking habits, with pyrolytic liners suited for infrequent deep cleaning and catalytic liners for ongoing, low-effort upkeep.
Pyrolytic vs Catalytic liners for cleaning Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com