Fuzzy logic rice cookers use advanced algorithms to adjust cooking time and temperature based on variables like rice type and moisture levels, ensuring consistent results. Induction heating rice cookers employ electromagnetic fields to heat the entire inner pot evenly, providing faster cooking and precise temperature control. While fuzzy logic enhances adaptability and customization, induction heating offers superior heat distribution and efficiency for perfect rice texture.
Table of Comparison
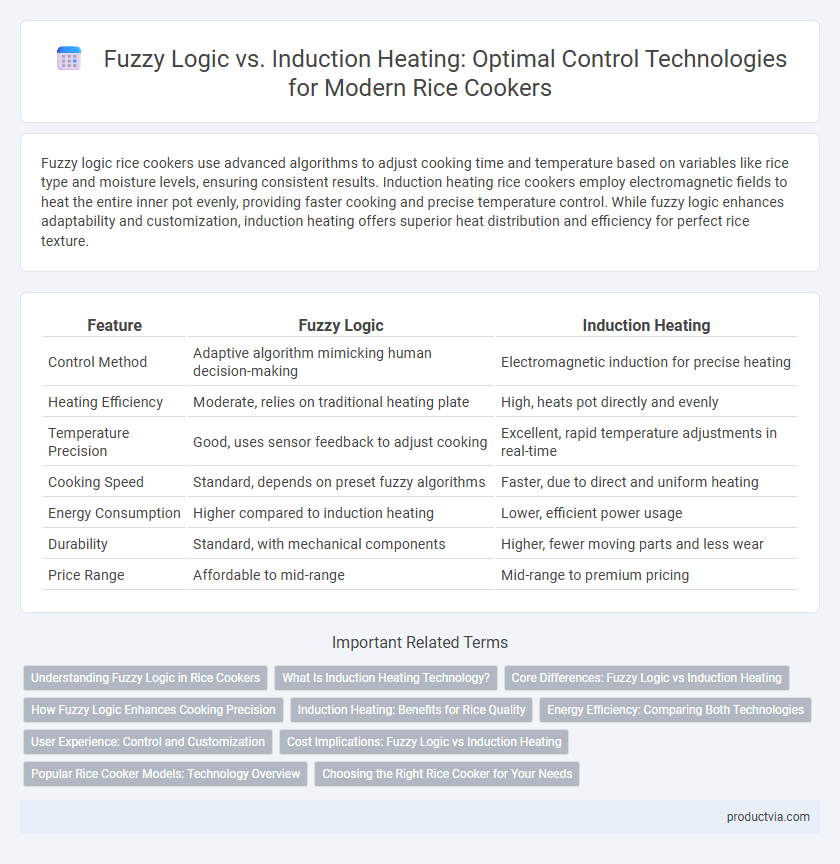
| Feature | Fuzzy Logic | Induction Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Control Method | Adaptive algorithm mimicking human decision-making | Electromagnetic induction for precise heating |
| Heating Efficiency | Moderate, relies on traditional heating plate | High, heats pot directly and evenly |
| Temperature Precision | Good, uses sensor feedback to adjust cooking | Excellent, rapid temperature adjustments in real-time |
| Cooking Speed | Standard, depends on preset fuzzy algorithms | Faster, due to direct and uniform heating |
| Energy Consumption | Higher compared to induction heating | Lower, efficient power usage |
| Durability | Standard, with mechanical components | Higher, fewer moving parts and less wear |
| Price Range | Affordable to mid-range | Mid-range to premium pricing |
Understanding Fuzzy Logic in Rice Cookers
Fuzzy logic in rice cookers allows for precise adjustments of cooking time and temperature by mimicking human decision-making, resulting in perfectly cooked rice with minimal user input. Unlike induction heating, which relies on magnetic fields for rapid and uniform heat distribution, fuzzy logic enhances control algorithms to adapt dynamically to different rice types and quantities. This intelligent control system optimizes texture and moisture levels, ensuring consistent cooking performance.
What Is Induction Heating Technology?
Induction heating technology in rice cookers uses electromagnetic fields to directly heat the inner pot, providing precise temperature control and faster cooking times compared to traditional methods. This technology enhances energy efficiency by producing heat only in the pot, minimizing heat loss and ensuring even cooking of rice. Unlike fuzzy logic controls that adjust cooking based on sensor feedback, induction heating offers superior responsiveness and consistency in temperature management for optimal rice texture.
Core Differences: Fuzzy Logic vs Induction Heating
Fuzzy logic in rice cookers uses advanced algorithms to adjust cooking time and temperature based on variables like rice type and moisture, providing precise control for optimal texture. Induction heating employs electromagnetic fields to directly heat the pot, resulting in faster, more even temperature distribution and enhanced cooking efficiency. The core difference lies in fuzzy logic's intelligent control system versus induction heating's superior heat generation method.
How Fuzzy Logic Enhances Cooking Precision
Fuzzy logic in rice cookers enhances cooking precision by continuously adjusting temperature and cooking time based on real-time feedback from sensors, allowing for more accurate control of heat levels compared to induction heating's consistent magnetic heat profile. This dynamic adjustment helps achieve ideal texture and moisture in rice by mimicking human decision-making processes and responding to variables like rice type and water quantity. Fuzzy logic's adaptive algorithms improve cooking outcomes, especially in varied conditions, making it superior for delicate rice preparations.
Induction Heating: Benefits for Rice Quality
Induction heating rice cookers provide precise temperature control by using electromagnetic fields to directly heat the inner pot, resulting in even cooking and enhanced rice texture. This advanced technology maintains consistent heat distribution, improving water absorption and maximizing the rice's natural flavors and aroma. Compared to fuzzy logic systems, induction heating offers superior efficiency and faster cooking times, ensuring optimal rice quality with every batch.
Energy Efficiency: Comparing Both Technologies
Fuzzy logic rice cookers adjust cooking parameters based on real-time sensor data, optimizing energy use by preventing overcooking and reducing power consumption through adaptive heat control. Induction heating rice cookers use electromagnetic fields to heat the cooking pot directly, providing rapid and precise temperature adjustments that lead to lower energy waste and faster cooking times. Induction heating generally offers superior energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and maintaining consistent heat distribution compared to fuzzy logic models.
User Experience: Control and Customization
Fuzzy logic rice cookers provide precise cooking adjustments by analyzing temperature and humidity to optimize cooking stages, enhancing user experience through adaptive control and customizable settings. Induction heating rice cookers offer rapid, even heating with precise temperature control, delivering consistent results and allowing users to customize cooking modes for various rice types. Both technologies improve user satisfaction, but induction heating excels in speed and uniform heat distribution, while fuzzy logic emphasizes intelligent decision-making for personalized cooking.
Cost Implications: Fuzzy Logic vs Induction Heating
Fuzzy logic rice cookers generally have lower manufacturing costs compared to induction heating models due to simpler electronic components and control systems. Induction heating technology requires advanced sensors and high-power electromagnetic coils, increasing production expenses and retail prices. The higher initial cost of induction heating cookers is often offset by better cooking precision and energy efficiency, influencing long-term value for consumers.
Popular Rice Cooker Models: Technology Overview
Popular rice cooker models utilizing fuzzy logic incorporate advanced microcomputer control to adjust temperature and cooking time dynamically, ensuring precise and consistent results for various rice types. Induction heating rice cookers leverage electromagnetic fields to heat the entire inner pot evenly, providing faster cooking and superior temperature control compared to traditional heating elements. Leading brands like Zojirushi and Panasonic offer models with both technologies, with induction heating often preferred for its efficiency and enhanced cooking performance.
Choosing the Right Rice Cooker for Your Needs
Fuzzy logic rice cookers use micro-computers to adjust temperature and cooking time precisely, ensuring perfectly cooked rice by mimicking human decision-making. Induction heating rice cookers provide powerful, uniform heat by directly heating the pot with electromagnetic energy, resulting in faster cooking and enhanced texture control. Choosing between fuzzy logic and induction heating depends on your preference for precision cooking versus high-performance heating efficiency.
Fuzzy logic vs induction heating for rice cooker controls Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com