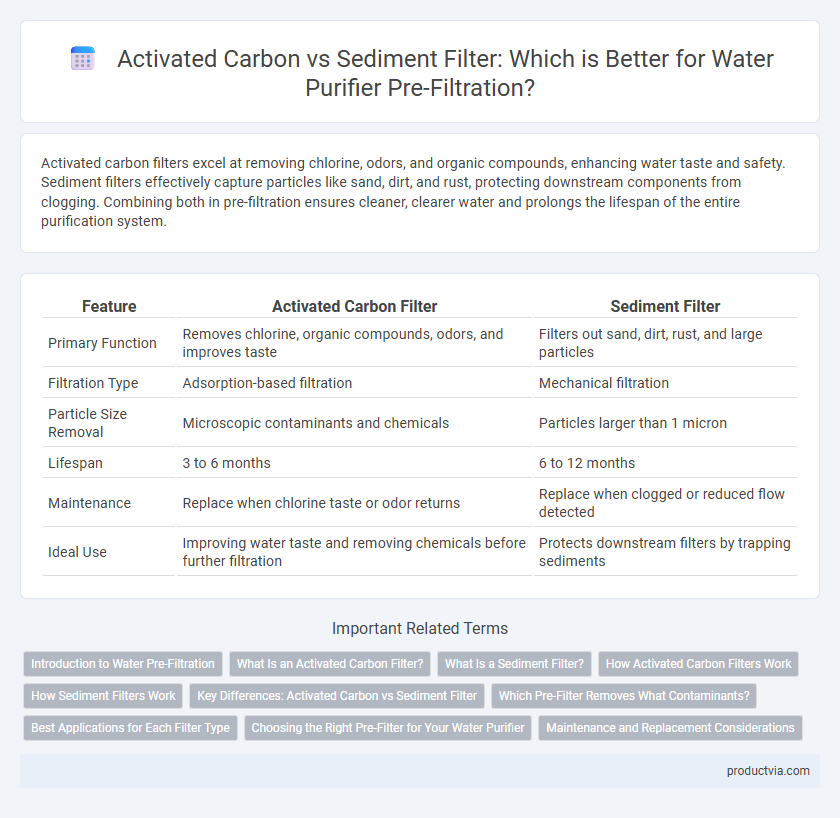
Activated carbon filters excel at removing chlorine, odors, and organic compounds, enhancing water taste and safety. Sediment filters effectively capture particles like sand, dirt, and rust, protecting downstream components from clogging. Combining both in pre-filtration ensures cleaner, clearer water and prolongs the lifespan of the entire purification system.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Activated Carbon Filter | Sediment Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Removes chlorine, organic compounds, odors, and improves taste | Filters out sand, dirt, rust, and large particles |
| Filtration Type | Adsorption-based filtration | Mechanical filtration |
| Particle Size Removal | Microscopic contaminants and chemicals | Particles larger than 1 micron |
| Lifespan | 3 to 6 months | 6 to 12 months |
| Maintenance | Replace when chlorine taste or odor returns | Replace when clogged or reduced flow detected |
| Ideal Use | Improving water taste and removing chemicals before further filtration | Protects downstream filters by trapping sediments |
Introduction to Water Pre-Filtration
Activated carbon and sediment filters play essential roles in water pre-filtration by targeting different contaminants to enhance overall purification. Sediment filters primarily remove physical particles such as dirt, sand, and rust, preventing clogging and extending the lifespan of downstream filters. Activated carbon filters adsorb organic compounds, chlorine, and unpleasant odors, improving water taste and protecting sensitive filtration components from chemical damage.
What Is an Activated Carbon Filter?
An activated carbon filter uses porous carbon material to trap contaminants through adsorption, effectively removing chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and unpleasant odors from water. Unlike sediment filters that primarily capture large particles like sand, dirt, and rust, activated carbon filters target chemical impurities and improve water taste and smell. This filtration stage is crucial in pre-filtration systems to enhance overall water quality before advanced treatments.
What Is a Sediment Filter?
A sediment filter is designed to remove large particles such as sand, dirt, rust, and silt from water, ensuring cleaner and clearer water before it enters further filtration stages. Unlike activated carbon filters that target chemicals, odors, and chlorine, sediment filters primarily protect water purification systems by preventing debris buildup and damage. Installing a sediment filter as a pre-filtration step enhances the lifespan and efficiency of more delicate filters in water purifiers.
How Activated Carbon Filters Work
Activated carbon filters remove contaminants through adsorption, where pollutants like chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and bad odors bind to the porous surface of the activated carbon. This process improves water taste and eliminates harmful chemicals that sediment filters cannot trap, as sediment filters only block larger particles such as dirt and rust. Activated carbon's high surface area and porous structure make it highly efficient in targeting chemical impurities during pre-filtration in water purification systems.
How Sediment Filters Work
Sediment filters work by physically trapping and removing particles such as dirt, sand, rust, and other large contaminants from water through a fine mesh or porous material. Unlike activated carbon filters that adsorb chemical impurities and improve taste and odor, sediment filters primarily protect downstream purification components by preventing clogging and damage. Their efficiency depends on micron ratings, with common sizes ranging from 1 to 50 microns, effectively capturing suspended solids before water passes to further filtration stages.
Key Differences: Activated Carbon vs Sediment Filter
Activated carbon filters excel at removing chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and improving taste and odor by adsorbing chemical impurities, whereas sediment filters primarily target physical particles like sand, dirt, and rust to prevent clogging and damage in subsequent filtration stages. Activated carbon is made from carbon-rich materials treated to create a porous structure for adsorption, while sediment filters typically utilize polypropylene or cellulose fibers to trap larger solid particulates. Choosing between activated carbon and sediment pre-filters depends on water quality concerns: sediment filters are essential for turbidity reduction, whereas activated carbon filters are critical for chemical contaminant removal.
Which Pre-Filter Removes What Contaminants?
Activated carbon pre-filters effectively remove chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, and unpleasant odors from water, improving taste and odor quality. Sediment filters target physical particles such as sand, dirt, rust, and silt, preventing these larger contaminants from entering the purification system. Selecting the appropriate pre-filter depends on the specific contaminants present in the water source, ensuring optimal protection and longevity for the main filtration components.
Best Applications for Each Filter Type
Activated carbon filters excel in pre-filtration by removing chlorine, organic compounds, and unpleasant odors, making them ideal for improving taste and protecting reverse osmosis membranes in residential water purification systems. Sediment filters specialize in capturing larger particles such as sand, rust, and dirt, preventing clogging and extending the lifespan of downstream filtration components in well or municipal water setups. Choosing the appropriate filter depends on the primary contaminants present, with activated carbon suited for chemical and taste issues, and sediment filters best for particulate removal.
Choosing the Right Pre-Filter for Your Water Purifier
Activated carbon filters excel at removing chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and unpleasant odors, enhancing water taste and safety. Sediment filters effectively trap particles like sand, rust, and dirt, protecting downstream components and extending the purifier's lifespan. Selecting the right pre-filter depends on your source water quality: sediment filters are ideal for physically heavy contaminants, while activated carbon is best for chemical impurities.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Activated carbon filters require regular replacement every 6 to 12 months to maintain effective adsorption of chlorine, odors, and organic compounds, while sediment filters primarily need replacement based on visible clogging or reduced water flow, often every 3 to 6 months. Maintenance of activated carbon filters involves monitoring for reduced taste and odor removal efficiency, whereas sediment filters demand periodic cleaning or replacement to prevent sediment buildup that can damage downstream components. Choosing the right pre-filtration depends on the specific water quality and maintenance convenience, as activated carbon filters tend to have higher upkeep costs compared to sediment filters.
Activated carbon vs sediment filter for pre-filtration Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com