UF membranes in water purifiers effectively remove suspended solids, bacteria, and viruses while retaining essential minerals, offering a natural taste. NF membranes provide a higher level of filtration by removing dissolved salts, heavy metals, and organic compounds, ideal for water with high hardness or contamination. Choosing between UF and NF membranes depends on water quality and purification needs, balancing mineral retention with contaminant removal.
Table of Comparison
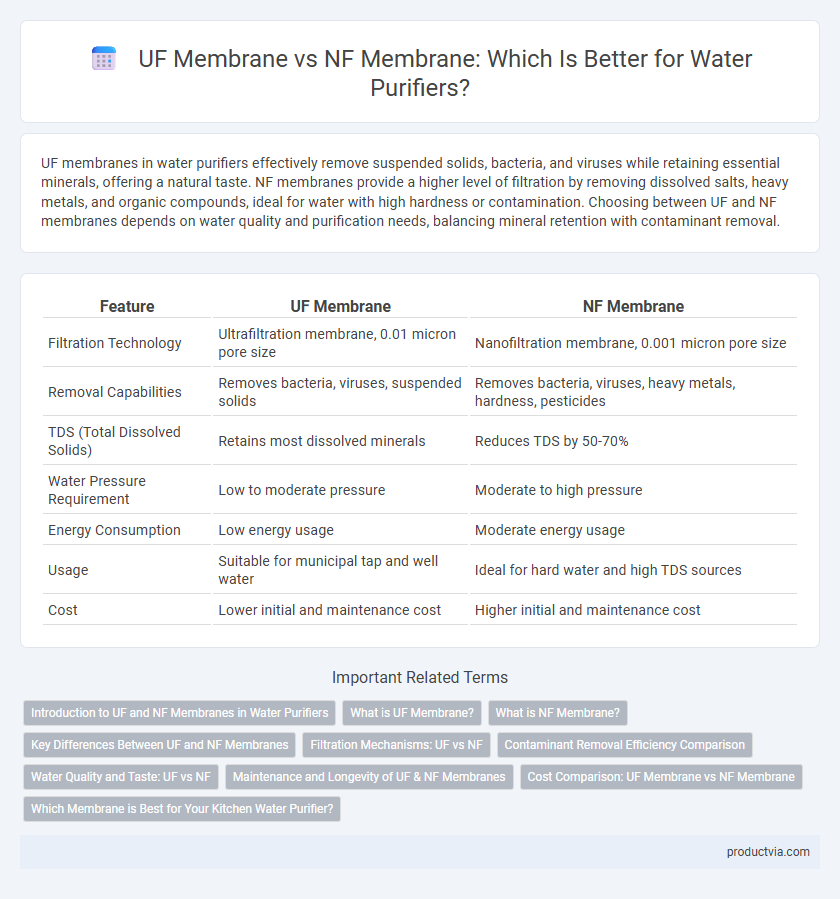
| Feature | UF Membrane | NF Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Technology | Ultrafiltration membrane, 0.01 micron pore size | Nanofiltration membrane, 0.001 micron pore size |
| Removal Capabilities | Removes bacteria, viruses, suspended solids | Removes bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, hardness, pesticides |
| TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) | Retains most dissolved minerals | Reduces TDS by 50-70% |
| Water Pressure Requirement | Low to moderate pressure | Moderate to high pressure |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy usage | Moderate energy usage |
| Usage | Suitable for municipal tap and well water | Ideal for hard water and high TDS sources |
| Cost | Lower initial and maintenance cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost |
Introduction to UF and NF Membranes in Water Purifiers
Ultrafiltration (UF) membranes in water purifiers use pore sizes typically between 0.01 to 0.1 microns, effectively removing bacteria, viruses, and suspended solids without eliminating essential minerals. Nanofiltration (NF) membranes feature slightly smaller pore sizes around 0.001 to 0.01 microns, enabling them to reduce heavy metals, hardness-causing salts, and some organic compounds while retaining beneficial minerals. Both UF and NF membranes improve water quality but differ in filtration precision and their impact on mineral retention.
What is UF Membrane?
UF membrane, or Ultrafiltration membrane, is a water purification technology that uses a pressure-driven process to remove suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, and high molecular weight organic compounds from water. It operates with pore sizes typically between 0.01 and 0.1 microns, effectively filtering out contaminants while retaining essential minerals. UF membranes require lower pressure compared to NF membranes, making them energy-efficient and ideal for households seeking safe, clean drinking water without extensive chemical treatment.
What is NF Membrane?
NF membrane, or Nanofiltration membrane, is a semi-permeable filter designed to remove divalent and larger monovalent ions, organic compounds, and pathogens from water while allowing essential minerals like calcium and magnesium to pass through. It operates with pore sizes ranging from 1 to 10 nanometers, providing effective filtration for water softening, fluoride removal, and partial desalination. NF membranes are commonly used in water purifiers to improve taste, reduce hardness, and retain beneficial minerals, offering a balance between filtration efficiency and water quality.
Key Differences Between UF and NF Membranes
UF membranes filter out particles, bacteria, and viruses with pore sizes typically ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 microns, making them ideal for removing suspended solids and microorganisms. NF membranes have smaller pore sizes around 0.001 to 0.01 microns, effectively blocking divalent and larger monovalent ions, organic molecules, and certain salts, which enhances water softening and contaminant removal. The key difference lies in NF's ability to reject dissolved salts and organic compounds while UF primarily targets particles and microbes.
Filtration Mechanisms: UF vs NF
Ultrafiltration (UF) membranes use a physical barrier that filters water through pore sizes typically between 0.01 and 0.1 microns, effectively removing bacteria, viruses, and suspended solids without altering dissolved minerals. Nanofiltration (NF) membranes have smaller pores around 0.001 microns, enabling partial removal of multivalent ions and organic molecules while allowing monovalent ions like sodium and chloride to pass through. UF membranes operate primarily on size exclusion, whereas NF membranes employ both size exclusion and charge repulsion to achieve selective filtration.
Contaminant Removal Efficiency Comparison
UF membranes effectively remove suspended solids, bacteria, and viruses due to their pore size ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 microns, but they do not eliminate dissolved salts or heavy metals. NF membranes offer superior contaminant removal by filtering out divalent and larger monovalent ions, organic compounds, and more than 90% of heavy metals such as lead and arsenic. The choice between UF and NF membranes depends on the specific water quality requirements, with NF membranes providing enhanced purification for water with higher levels of dissolved contaminants.
Water Quality and Taste: UF vs NF
UF membranes effectively remove suspended particles, bacteria, and viruses, preserving essential minerals that enhance water's natural taste. NF membranes filter out smaller contaminants, including certain salts and organic molecules, resulting in water with reduced hardness and slightly altered taste due to mineral removal. Both membranes improve water quality, but UF maintains more natural flavor by retaining beneficial minerals, while NF offers higher purification with a crisper taste profile.
Maintenance and Longevity of UF & NF Membranes
UF membranes require less frequent cleaning and have a longer lifespan due to their larger pore sizes, which reduce clogging and fouling compared to NF membranes. NF membranes need more regular maintenance to prevent scaling and biofouling, as their smaller pores trap more contaminants. Proper pre-treatment of water and regular backwashing extend the durability of both UF and NF membranes, but UF membranes generally offer lower operational costs over time.
Cost Comparison: UF Membrane vs NF Membrane
UF membranes for water purifiers generally cost less upfront compared to NF membranes due to simpler manufacturing processes and materials. NF membranes, while more expensive initially, offer better removal of dissolved salts and organic compounds, providing enhanced purification that may justify the higher price in long-term usage. Maintenance costs for UF membranes tend to be lower, but NF membranes require more frequent cleaning and replacement, impacting overall cost-efficiency.
Which Membrane is Best for Your Kitchen Water Purifier?
UF membranes effectively remove suspended solids, bacteria, and viruses, making them ideal for areas with low TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) water sources. NF membranes filter out dissolved salts, heavy metals, and organic compounds, providing superior purification for water with higher TDS levels. Choosing the best membrane for your kitchen water purifier depends on your water quality; UF is suitable for pre-treated or low TDS water, while NF delivers comprehensive filtration for hard and contaminated water sources.
UF membrane vs NF membrane for water purifier Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com