Condensation drying in dishwashers uses natural cooling to remove moisture, making it an energy-efficient and gentle option for delicate items and plastic pet dishes. Heated drying, on the other hand, employs an internal heating element to speed up the drying process, ensuring faster results but consuming more electricity and posing a higher risk of warping or damage to certain materials. Choosing between condensation drying and heated drying depends on balancing energy consumption, drying speed, and the types of pet dishes being cleaned.
Table of Comparison
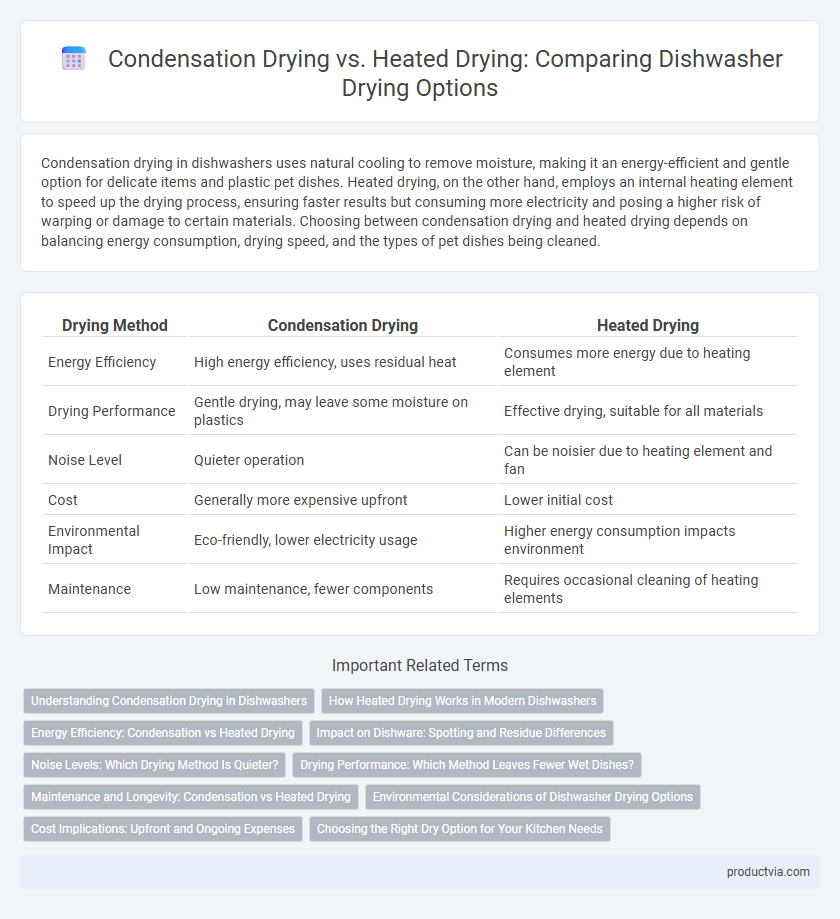
| Drying Method | Condensation Drying | Heated Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High energy efficiency, uses residual heat | Consumes more energy due to heating element |
| Drying Performance | Gentle drying, may leave some moisture on plastics | Effective drying, suitable for all materials |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Can be noisier due to heating element and fan |
| Cost | Generally more expensive upfront | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, lower electricity usage | Higher energy consumption impacts environment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, fewer components | Requires occasional cleaning of heating elements |
Understanding Condensation Drying in Dishwashers
Condensation drying in dishwashers leverages the natural process of heat transfer, where heated water vapor condenses on cooler stainless steel walls, effectively drying dishes without additional energy for heating elements. This method reduces energy consumption and is quieter compared to heated drying, making it an eco-friendly and energy-efficient option. However, condensation drying may leave some plastics damp due to lower drying temperatures, highlighting the importance of material considerations in dishwasher performance.
How Heated Drying Works in Modern Dishwashers
Heated drying in modern dishwashers uses an electric heating element to raise the temperature inside the tub, evaporating moisture quickly from dishes. This method efficiently eliminates water droplets by accelerating the drying process, ensuring dishes are ready to use immediately after the cycle ends. Many models also feature sensors that adjust the heater's power to optimize energy consumption while maintaining effective drying performance.
Energy Efficiency: Condensation vs Heated Drying
Condensation drying in dishwashers uses residual heat to evaporate water, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to heated drying, which relies on electric heating elements to actively dry dishes. Energy efficiency ratings typically favor condensation drying due to its lower electricity use and environmentally friendly operation. Choosing a dishwasher with condensation drying technology can lead to noticeable savings on energy bills while maintaining effective drying performance.
Impact on Dishware: Spotting and Residue Differences
Condensation drying in dishwashers uses a cooler rinse and relies on natural evaporation, reducing the risk of spotting and minimizing residue on glassware and plastic items. Heated drying involves higher temperatures that can cause water droplets to evaporate quickly, often leaving mineral spots and streaks on dishware, especially in hard water areas. Choosing condensation drying improves the longevity and appearance of delicate items by preventing heat damage and reducing unsightly residues.
Noise Levels: Which Drying Method Is Quieter?
Condensation drying in dishwashers operates quietly by relying on natural heat transfer, producing significantly less noise compared to heated drying, which uses a heating element that can emit a humming or buzzing sound. The absence of a fan or additional mechanical components in condensation drying further reduces noise levels, making it the preferred choice for quieter kitchens. Models with condensation drying typically score lower on noise level ratings, ranging from 40 to 50 decibels, whereas heated drying systems often operate around 50 to 60 decibels or higher.
Drying Performance: Which Method Leaves Fewer Wet Dishes?
Condensation drying uses residual heat and cool water to evaporate moisture, resulting in fewer water spots and generally leaving dishes drier compared to heated drying. Heated drying employs a heating element to actively dry dishes, but it can sometimes leave plastic items damp due to lower heat retention. Overall, condensation drying tends to offer superior drying performance for glassware and plastics, minimizing moisture and improving final dish dryness.
Maintenance and Longevity: Condensation vs Heated Drying
Condensation drying in dishwashers promotes longer appliance lifespan by using natural cooling processes that reduce wear on heating elements and minimize energy consumption. Heated drying often requires more frequent maintenance due to heat element degradation and increased risk of mold or residue buildup from trapped moisture. Choosing condensation drying enhances overall durability and lowers maintenance needs, optimizing dishwasher efficiency over time.
Environmental Considerations of Dishwasher Drying Options
Condensation drying uses residual heat to evaporate water, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to heated drying, which relies on electric heating elements that increase electricity use and greenhouse gas emissions. Selecting condensation drying helps lower a dishwasher's carbon footprint by conserving energy and minimizing the release of pollutants associated with power generation. Environmental sustainability improves as condensation drying technologies promote efficient resource use and reduce overall household energy demands.
Cost Implications: Upfront and Ongoing Expenses
Condensation drying in dishwashers typically incurs lower upfront costs due to simpler technology and reduced energy consumption, making it more budget-friendly initially. Heated drying involves higher initial expenses for heating elements and increased ongoing electricity costs, driving up total ownership expenses. Choosing condensation drying can result in long-term savings on energy bills, while heated drying may require higher maintenance and operational costs.
Choosing the Right Dry Option for Your Kitchen Needs
Condensation drying uses cooler air and fan circulation to condense moisture on the dishwasher walls, making it energy-efficient and quieter, ideal for eco-conscious kitchens. Heated drying employs a heating element to rapidly evaporate water, providing faster and more thorough drying results, which suits households needing quick cycle completion. Selecting the right dry option depends on balancing energy consumption, noise levels, and drying speed based on your kitchen's usage patterns and preferences.
Condensation Drying vs Heated Drying for Dishwasher Dry Options Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com