Fast freezing preserves food quality by rapidly lowering the temperature, which prevents the formation of large ice crystals that can damage cell structure. Regular freezing is slower, often resulting in larger ice crystals that degrade texture and flavor over time. Choosing fast freeze enhances nutrient retention and extends the shelf life of perishable items more effectively than regular freeze.
Table of Comparison
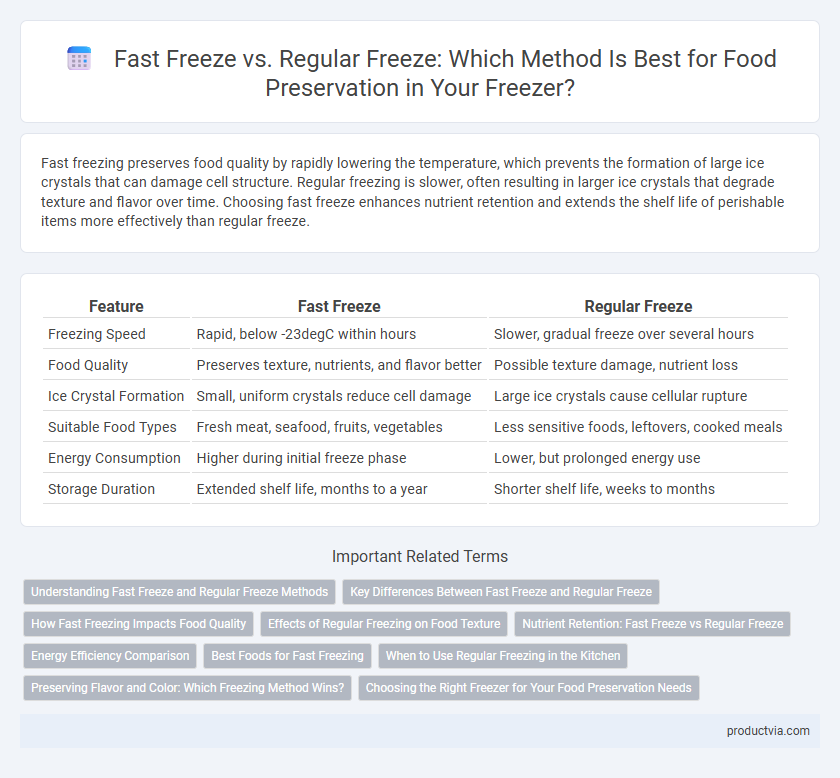
| Feature | Fast Freeze | Regular Freeze |
|---|---|---|
| Freezing Speed | Rapid, below -23degC within hours | Slower, gradual freeze over several hours |
| Food Quality | Preserves texture, nutrients, and flavor better | Possible texture damage, nutrient loss |
| Ice Crystal Formation | Small, uniform crystals reduce cell damage | Large ice crystals cause cellular rupture |
| Suitable Food Types | Fresh meat, seafood, fruits, vegetables | Less sensitive foods, leftovers, cooked meals |
| Energy Consumption | Higher during initial freeze phase | Lower, but prolonged energy use |
| Storage Duration | Extended shelf life, months to a year | Shorter shelf life, weeks to months |
Understanding Fast Freeze and Regular Freeze Methods
Fast freeze method rapidly lowers food temperature, causing smaller ice crystals to form, which preserves cellular structure and maintains texture, flavor, and nutritional value more effectively than regular freeze. Regular freeze lowers temperature slowly, leading to larger ice crystals that can rupture cell walls, resulting in potential quality degradation such as drip loss and texture changes upon thawing. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the appropriate freezing technique to optimize food preservation and extend shelf life.
Key Differences Between Fast Freeze and Regular Freeze
Fast freeze technology rapidly lowers food temperature, forming smaller ice crystals that preserve cellular structure and maintain texture, flavor, and nutritional value better than regular freeze methods. Regular freeze cools food more slowly, resulting in larger ice crystals that can damage cell walls, leading to moisture loss and compromised taste and quality over time. The key difference lies in the freezing speed, which directly impacts food integrity and shelf life in preservation processes.
How Fast Freezing Impacts Food Quality
Fast freezing preserves food quality by rapidly lowering the temperature, which prevents the formation of large ice crystals that can damage cellular structure. This process retains the texture, flavor, and nutritional value better than regular freezing, which causes slower ice crystal growth and potential moisture loss. Maintaining small ice crystals during fast freeze minimizes cell rupture and reduces drip loss upon thawing, ensuring superior food preservation.
Effects of Regular Freezing on Food Texture
Regular freezing slows the freezing process, causing larger ice crystals to form within food cells, which can rupture cell walls and lead to a softer, mushier texture upon thawing. This textural degradation is especially noticeable in high-water-content foods like fruits, vegetables, and seafood. Maintaining optimal freezer temperatures around -18degC helps mitigate, but does not fully prevent, the negative impact on food texture caused by slower crystal formation during regular freezing.
Nutrient Retention: Fast Freeze vs Regular Freeze
Fast freeze technology rapidly lowers food temperature, minimizing ice crystal formation and preserving cell structure, which significantly enhances nutrient retention compared to regular freeze methods. Regular freezing results in larger ice crystals that can rupture cell walls, leading to nutrient loss and compromised texture. Studies show fast freezing retains higher levels of vitamins C and B, antioxidants, and enzymes, maintaining the food's original nutritional profile more effectively.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Fast freeze technology rapidly lowers food temperature, minimizing ice crystal formation and preserving texture while consuming slightly more energy per cycle than regular freeze methods. Regular freeze cycles operate at a slower rate, using less immediate power but potentially increasing overall energy use due to longer compressor run times to achieve target temperatures. Energy efficiency in food preservation depends on balancing faster initial energy input with reduced spoilage and improved food quality, often making fast freeze systems more cost-effective in the long term.
Best Foods for Fast Freezing
Fast freezing rapidly reduces the temperature of food to below -18degC, forming smaller ice crystals that better preserve texture and nutrient content compared to regular freezing. Best foods for fast freezing include fruits like berries, vegetables such as peas and corn, and seafood like fish fillets, as they retain freshness and flavor more effectively. Meats and pre-cooked meals also benefit from fast freezing by minimizing moisture loss and preventing cellular damage.
When to Use Regular Freezing in the Kitchen
Regular freezing is ideal for storing foods such as cooked meals, raw meat cuts, and fruits when immediate hard freezing is not required, allowing gradual temperature reduction to maintain texture and flavor. It is best used for foods with high moisture content or delicate structure that may be damaged by rapid ice crystal formation during fast freeze. Employing regular freezing helps preserve nutrient integrity and extends shelf life without compromising the food's natural quality.
Preserving Flavor and Color: Which Freezing Method Wins?
Fast freeze technology preserves food flavor and color more effectively by rapidly reducing temperature, minimizing ice crystal formation that damages cell walls. Regular freeze methods cause slower ice crystal growth, leading to moisture loss and dulling of natural flavors and vibrant colors. Studies show fast freezing maintains nutrient integrity and sensory qualities, making it superior for high-quality food preservation.
Choosing the Right Freezer for Your Food Preservation Needs
Fast freeze technology rapidly lowers the temperature of food to -18degC or below within two hours, preserving texture, flavor, and nutrients more effectively than regular freeze methods, which typically take longer to reach the same temperature. Choosing a freezer with quick-freeze capabilities minimizes ice crystal formation, reducing cellular damage in meats, fruits, and vegetables, ensuring fresher taste and longer shelf life. For optimal food preservation, prioritize freezers with adjustable fast freeze settings and energy-efficient compressors designed to maintain consistent ultra-low temperatures.
Fast freeze vs Regular freeze for food preservation Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com