Ferritic steel is highly compatible with induction stoves due to its magnetic properties, ensuring efficient heat transfer and quick cooking. Austenitic steel, commonly found in stainless cookware, lacks sufficient magnetism and often requires a ferromagnetic base layer to work effectively on induction cooktops. Choosing ferritic steel cookware guarantees better performance and seamless compatibility with induction stove pets.
Table of Comparison
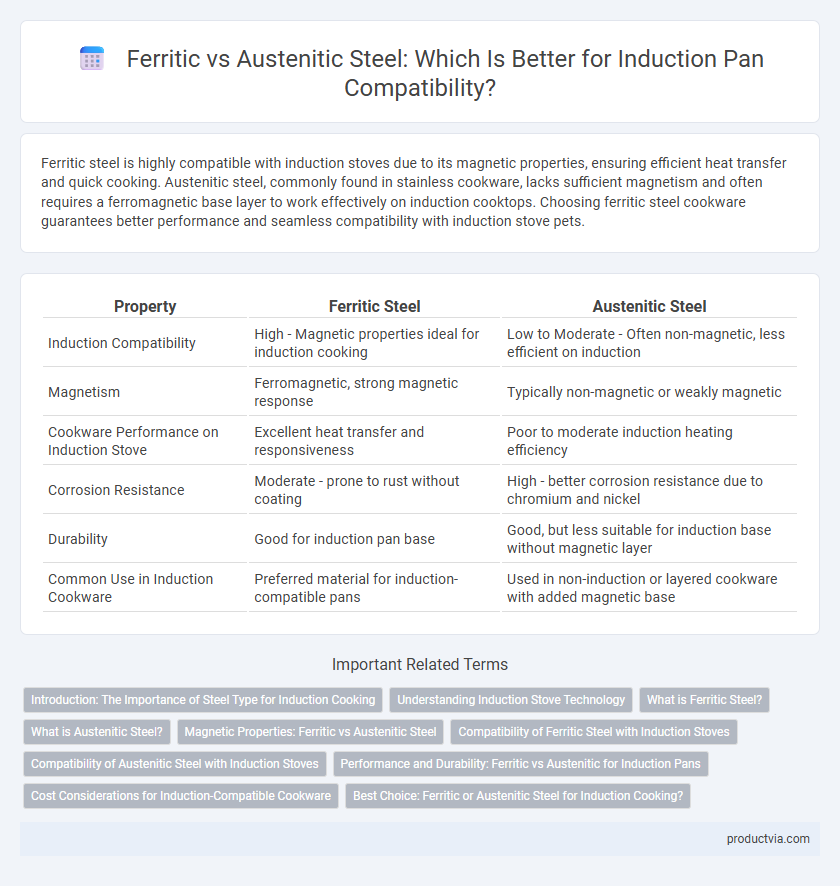
| Property | Ferritic Steel | Austenitic Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Compatibility | High - Magnetic properties ideal for induction cooking | Low to Moderate - Often non-magnetic, less efficient on induction |
| Magnetism | Ferromagnetic, strong magnetic response | Typically non-magnetic or weakly magnetic |
| Cookware Performance on Induction Stove | Excellent heat transfer and responsiveness | Poor to moderate induction heating efficiency |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate - prone to rust without coating | High - better corrosion resistance due to chromium and nickel |
| Durability | Good for induction pan base | Good, but less suitable for induction base without magnetic layer |
| Common Use in Induction Cookware | Preferred material for induction-compatible pans | Used in non-induction or layered cookware with added magnetic base |
Introduction: The Importance of Steel Type for Induction Cooking
Ferritic steel, with its high magnetic permeability, ensures optimal compatibility with induction stoves by efficiently generating the magnetic field required for heating. Austenitic steel, commonly found in stainless steel cookware, lacks sufficient magnetic properties, often resulting in poor induction performance unless specially treated. Selecting ferritic steel pans maximizes heat transfer efficiency and energy savings on induction cooktops.
Understanding Induction Stove Technology
Ferritic steel exhibits higher magnetic permeability than austenitic steel, making it more compatible with induction stove technology by efficiently transferring electromagnetic energy to the pan. Austenitic steel, often non-magnetic due to its crystalline structure, generally performs poorly on induction cooktops unless specifically engineered with magnetic properties. Understanding the magnetic characteristics of ferritic versus austenitic steel is crucial for selecting cookware that maximizes heat transfer and cooking efficiency on induction stoves.
What is Ferritic Steel?
Ferritic steel is a magnetic, iron-based alloy characterized by a body-centered cubic (BCC) crystal structure, making it highly compatible with induction stoves that rely on magnetic properties to generate heat. It typically contains low carbon content and chromium, providing good corrosion resistance and excellent thermal conductivity crucial for efficient cooking. Its magnetic nature ensures optimal electromagnetic induction, allowing pans made from ferritic steel to heat quickly and uniformly on induction cooktops.
What is Austenitic Steel?
Austenitic steel is a type of stainless steel characterized by its high chromium and nickel content, which gives it excellent corrosion resistance and toughness. Unlike ferritic steel, austenitic steel has a non-magnetic crystal structure, making it less compatible with induction cooktops that require magnetic cookware for efficient heating. However, some austenitic steels can be engineered to exhibit magnetic properties, allowing their use with induction stoves when properly designed.
Magnetic Properties: Ferritic vs Austenitic Steel
Ferritic steel exhibits high magnetic permeability, making it optimal for induction pan compatibility as it efficiently couples with the induction stove's magnetic field. Austenitic steel, characterized by low magnetic permeability due to its non-magnetic crystalline structure, often requires additional ferromagnetic layers or modifications to function effectively on induction cooktops. The distinct difference in magnetic properties between ferritic and austenitic steel critically influences the heating performance and energy efficiency of induction cookware.
Compatibility of Ferritic Steel with Induction Stoves
Ferritic steel exhibits strong magnetic properties essential for efficient heat generation on induction stoves, ensuring optimal compatibility. The high permeability of ferritic steel allows it to interact effectively with the induction cooktop's magnetic field, leading to rapid and uniform heating. Unlike austenitic steel, ferritic steel pans maintain consistent performance on induction stoves, making them the preferred choice for induction cookware.
Compatibility of Austenitic Steel with Induction Stoves
Austenitic steel, commonly found in stainless steel cookware, is generally less magnetic than ferritic steel, which affects its performance on induction stoves. Induction stoves require cookware with magnetic properties to efficiently generate heat; therefore, pure austenitic steel pans may not be compatible unless they have a magnetic base layer. Many manufacturers address this by bonding a ferritic steel plate to the bottom of austenitic steel pans, ensuring proper induction stove compatibility and optimal heating performance.
Performance and Durability: Ferritic vs Austenitic for Induction Pans
Ferritic steel exhibits better magnetic permeability, enhancing induction pan performance by ensuring efficient heat transfer and faster cooking times. Austenitic steel, while less magnetic, offers superior corrosion resistance and higher temperature durability, making it suitable for long-term use but potentially less efficient on induction cooktops. Selecting ferritic steel pans typically results in improved induction cooking responsiveness and longevity under frequent high-heat conditions.
Cost Considerations for Induction-Compatible Cookware
Ferritic steel is generally more cost-effective for induction-compatible cookware due to its simpler manufacturing process and magnetic properties that ensure efficient induction heating. Austenitic steel, often stainless steel like 304 or 316 grades, tends to be more expensive because of its higher corrosion resistance and non-magnetic nature, which requires additional layers to work with induction stoves. Selecting ferritic steel pans can significantly reduce cookware costs without compromising compatibility with induction cooktops.
Best Choice: Ferritic or Austenitic Steel for Induction Cooking?
Ferritic steel is the best choice for induction cooking due to its magnetic properties that ensure efficient heat transfer on induction stoves, while austenitic steel, commonly found in stainless steel cookware, lacks sufficient magnetic permeability and may not work effectively. Ferritic steel's high chromium content provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for induction-compatible pans. Choosing ferritic steel cookware guarantees optimal induction stove performance and energy efficiency.
Ferritic steel vs Austenitic steel for induction pan compatibility Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com