Ferritic steel is highly compatible with induction stoves due to its magnetic properties, which allow for efficient heat generation through electromagnetic induction. Austenitic steel, often non-magnetic, generally performs poorly on induction cooktops, leading to slower heating and reduced energy efficiency. For optimal induction stove use, cookware made from ferritic steel ensures rapid responsiveness and consistent cooking performance.
Table of Comparison
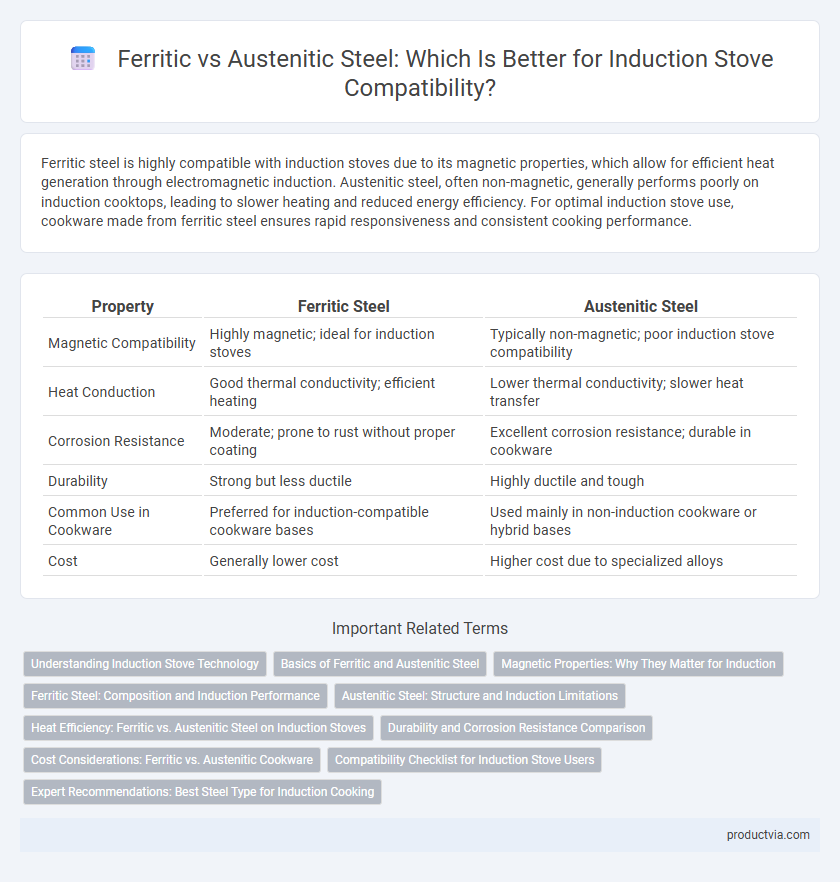
| Property | Ferritic Steel | Austenitic Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Compatibility | Highly magnetic; ideal for induction stoves | Typically non-magnetic; poor induction stove compatibility |
| Heat Conduction | Good thermal conductivity; efficient heating | Lower thermal conductivity; slower heat transfer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to rust without proper coating | Excellent corrosion resistance; durable in cookware |
| Durability | Strong but less ductile | Highly ductile and tough |
| Common Use in Cookware | Preferred for induction-compatible cookware bases | Used mainly in non-induction cookware or hybrid bases |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized alloys |
Understanding Induction Stove Technology
Ferritic steel offers superior compatibility with induction stoves due to its high magnetic permeability, enabling efficient electromagnetic field generation for rapid heating. Austenitic steel, typically less magnetic because of its crystalline structure, often requires added magnetic layers to enhance induction responsiveness. Understanding these material properties is crucial for optimizing cookware performance and energy efficiency in induction cooking technology.
Basics of Ferritic and Austenitic Steel
Ferritic steel contains a high amount of iron with magnetic properties, making it highly compatible with induction stoves due to its ability to efficiently generate heat via electromagnetic induction. Austenitic steel, commonly found in stainless steel cookware, lacks magnetic properties because of its chromium and nickel content, which reduces its induction stove compatibility. Understanding the magnetic permeability and chemical composition differences between ferritic and austenitic steel is crucial for selecting cookware that performs optimally on induction cooktops.
Magnetic Properties: Why They Matter for Induction
Ferritic steel's high magnetic permeability enhances its compatibility with induction stoves, as the magnetic field induces electric currents efficiently, generating heat effectively. Austenitic steel's low magnetic permeability results in poor induction heating, making it less suitable for induction cooktops. The core principle is that induction stoves rely on magnetic properties to transfer energy, so ferritic steel's magnetic responsiveness directly impacts cooking performance and energy efficiency.
Ferritic Steel: Composition and Induction Performance
Ferritic steel, primarily composed of iron with a high chromium content (10.5-30%), exhibits magnetic properties ideal for induction stove compatibility due to its body-centered cubic (BCC) crystal structure. This magnetic nature enhances electromagnetic field interaction, resulting in efficient heat generation and faster cooking times on induction cooktops. Unlike austenitic steel, ferritic steel's superior ferromagnetic response ensures consistent induction performance and energy efficiency.
Austenitic Steel: Structure and Induction Limitations
Austenitic steel, characterized by its face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure, exhibits low magnetic permeability, significantly impacting its compatibility with induction stoves. This metal's non-magnetic nature reduces eddy current generation, resulting in inefficient heat induction compared to ferritic steel, which has a body-centered cubic (BCC) structure and higher magnetic permeability. Consequently, cookware made from austenitic steel often requires a magnetic base or additional layers to enhance induction heating performance.
Heat Efficiency: Ferritic vs. Austenitic Steel on Induction Stoves
Ferritic steel exhibits higher heat efficiency on induction stoves due to its greater magnetic permeability, allowing better heat transfer and faster cooking times compared to austenitic steel. Austenitic steel, commonly used in stainless steel cookware, has lower magnetic responsiveness, which reduces induction stove compatibility and heat efficiency. Choosing ferritic steel cookware maximizes induction heating performance, ensuring optimal energy use and quicker temperature reach.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Ferritic steel offers superior magnetic permeability essential for induction stove compatibility, ensuring efficient heat transfer and durability under high temperatures. Its chromium content enhances corrosion resistance, making it more resistant to rust and surface degradation in kitchen environments compared to austenitic steel. Austenitic steel, while less magnetic and less efficient for induction heating, provides good corrosion resistance but lacks the same level of durability and magnetic responsiveness critical for induction stove performance.
Cost Considerations: Ferritic vs. Austenitic Cookware
Ferritic steel cookware is generally more cost-effective for induction stoves due to its higher magnetic permeability and lower production costs compared to austenitic steel. Austenitic steel, while offering superior corrosion resistance and durability, often commands a higher price because it requires additional alloying elements and complex manufacturing processes. Choosing ferritic steel can provide an affordable and efficient option without compromising induction compatibility.
Compatibility Checklist for Induction Stove Users
Ferritic steel is highly compatible with induction stoves due to its magnetic properties, ensuring efficient heat generation and energy savings. Austenitic steel, which is typically non-magnetic, often requires a ferritic base or specialized coatings to work effectively on induction cooktops. Users should verify cookware magnetic permeability and base flatness to guarantee optimal performance on induction stoves.
Expert Recommendations: Best Steel Type for Induction Cooking
Experts recommend ferritic steel over austenitic steel for induction stove compatibility due to its higher magnetic permeability, which ensures efficient heat generation. Ferritic steel's ferromagnetic properties align with the electromagnetic induction principle, making it ideal for quick and uniform heating. Austenitic steels lack sufficient magnetic response, resulting in poor performance on induction cooktops.
Ferritic steel vs austenitic steel for induction stove compatibility Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com