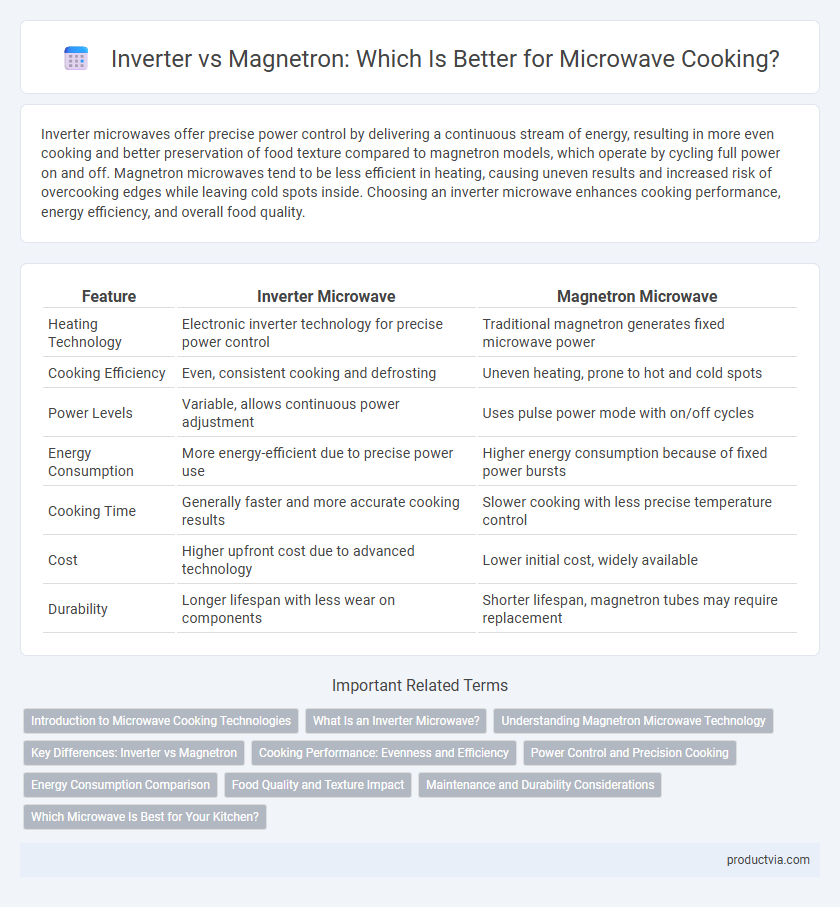
Inverter microwaves offer precise power control by delivering a continuous stream of energy, resulting in more even cooking and better preservation of food texture compared to magnetron models, which operate by cycling full power on and off. Magnetron microwaves tend to be less efficient in heating, causing uneven results and increased risk of overcooking edges while leaving cold spots inside. Choosing an inverter microwave enhances cooking performance, energy efficiency, and overall food quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inverter Microwave | Magnetron Microwave |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Technology | Electronic inverter technology for precise power control | Traditional magnetron generates fixed microwave power |
| Cooking Efficiency | Even, consistent cooking and defrosting | Uneven heating, prone to hot and cold spots |
| Power Levels | Variable, allows continuous power adjustment | Uses pulse power mode with on/off cycles |
| Energy Consumption | More energy-efficient due to precise power use | Higher energy consumption because of fixed power bursts |
| Cooking Time | Generally faster and more accurate cooking results | Slower cooking with less precise temperature control |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology | Lower initial cost, widely available |
| Durability | Longer lifespan with less wear on components | Shorter lifespan, magnetron tubes may require replacement |
Introduction to Microwave Cooking Technologies
Microwave cooking technologies primarily utilize two methods: inverter and magnetron systems, each influencing heating performance and energy efficiency. Magnetron microwaves generate microwave energy in pulses, causing uneven cooking and temperature fluctuations, whereas inverter microwaves deliver consistent energy output for precise temperature control and uniform heating. Inverter technology enhances cooking accuracy and texture retention, making it preferable for sensitive foods and advanced culinary applications.
What Is an Inverter Microwave?
An inverter microwave uses a variable power supply to deliver consistent and precise cooking power, allowing food to cook evenly without overcooking edges or undercooking centers. Unlike traditional magnetron microwaves that operate with full power cycles alternating between on and off, inverter technology enables continuous power adjustment for more efficient energy use and better texture retention. This makes inverter microwaves particularly effective for delicate tasks such as defrosting, simmering, and melting.
Understanding Magnetron Microwave Technology
Magnetron microwave technology generates microwaves by converting electrical energy into high-frequency radio waves using a magnetron tube, which directly heats food through dielectric heating. This traditional system cycles power on and off to control cooking intensity, often resulting in uneven heating and hot spots. Understanding the magnetron's operational mechanism highlights its cost-effectiveness and widespread use despite limitations compared to inverter technology, which offers continuous and precise power control for improved cooking performance.
Key Differences: Inverter vs Magnetron
Inverter microwaves deliver precise power control by continuously adjusting the power level, resulting in even cooking and better texture retention, while magnetron microwaves operate on fixed power cycles causing uneven heating. Inverter technology allows for gradual defrosting and delicate cooking, unlike magnetron systems that rely on switching the magnetron on and off at full power. Energy efficiency and consistent temperature regulation highlight the key advantages of inverter over traditional magnetron microwaves in modern kitchen appliances.
Cooking Performance: Evenness and Efficiency
Inverter microwaves deliver precise power control, resulting in more even cooking and consistent heating of food compared to magnetron microwaves, which operate at fixed power levels causing uneven hot spots. The inverter technology modulates energy flow, improving cooking efficiency by maintaining a steady temperature and reducing overcooking or undercooking. Magnetron microwaves, while traditional and cost-effective, lack the fine-tuned power adjustments that enhance cooking performance in inverter models.
Power Control and Precision Cooking
Inverter microwaves deliver consistent power by adjusting voltage to control cooking intensity, enabling precise temperature regulation and even heating. Magnetron microwaves operate on an on-off power cycle, causing fluctuations that may lead to uneven cooking and temperature spikes. The advanced power control of inverter technology improves cooking accuracy and preserves food texture better than traditional magnetron models.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Inverter microwaves use advanced power modulation technology to deliver consistent and precise energy output, resulting in more efficient cooking and lower energy consumption compared to traditional magnetron microwaves. Magnetron models operate at fixed power levels, frequently cycling on and off, which can cause energy waste and uneven cooking. Studies indicate inverter microwaves can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% while maintaining food quality.
Food Quality and Texture Impact
Inverter microwaves deliver consistent and precise power levels, resulting in evenly cooked food with better texture and moisture retention compared to traditional magnetron models that alternate between full power and off cycles. The continuous energy flow from inverter technology prevents overcooking or drying out delicate ingredients, preserving the natural flavors and tenderness of meals. Magnetron microwaves often produce uneven heating, leading to hot spots and compromised food quality, especially in dishes requiring gentle cooking.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Inverter microwaves feature solid-state electronics that reduce wear and tear, resulting in longer-lasting components and lower maintenance requirements compared to traditional magnetron models. Magnetrons rely on high-voltage tubes that may require periodic replacement due to their susceptibility to heat damage and wear over time. The advanced technology in inverter units allows for more consistent power output and improved reliability, minimizing the frequency and cost of repairs.
Which Microwave Is Best for Your Kitchen?
Inverter microwaves offer precise power control, enabling even cooking and defrosting by adjusting the energy level continuously, making them ideal for delicate dishes and energy efficiency. Magnetron microwaves operate with fixed power cycles, which can result in uneven heating but are generally more affordable and suitable for basic reheating needs. Choosing the best microwave depends on your cooking style and budget, with inverter models providing advanced performance for versatile kitchen use and magnetron models serving well for simple, everyday tasks.
Inverter vs Magnetron for microwave cooking Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com