Low-watt microwaves consume less electricity, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective for simple tasks like reheating and defrosting. High-watt microwaves, however, cook food faster due to their greater power, which can reduce overall cooking time and energy use despite higher wattage. Choosing between the two depends on balancing power needs with energy savings and cooking speed.
Table of Comparison
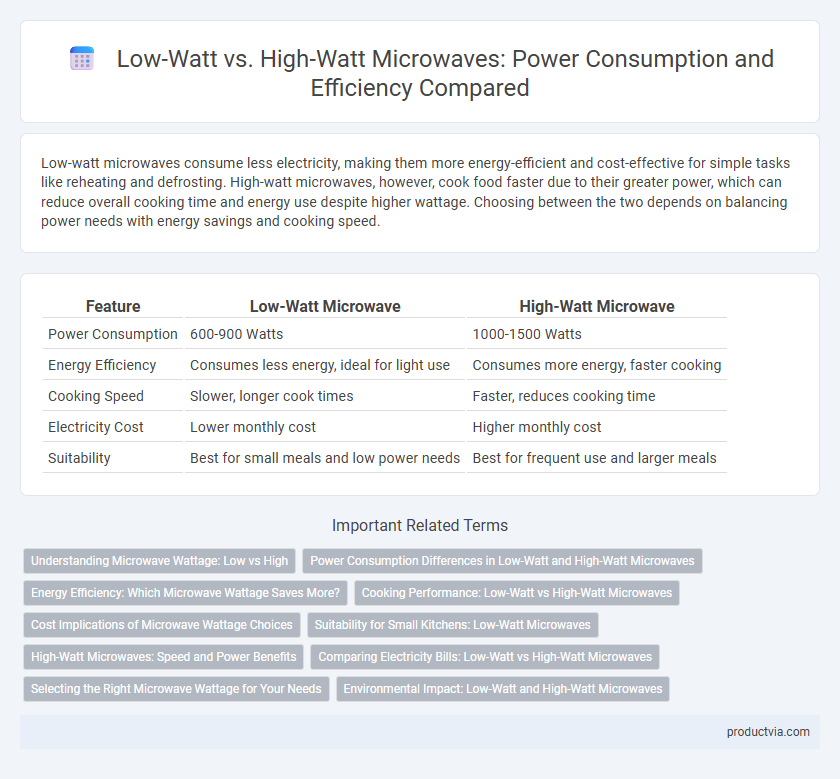
| Feature | Low-Watt Microwave | High-Watt Microwave |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | 600-900 Watts | 1000-1500 Watts |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes less energy, ideal for light use | Consumes more energy, faster cooking |
| Cooking Speed | Slower, longer cook times | Faster, reduces cooking time |
| Electricity Cost | Lower monthly cost | Higher monthly cost |
| Suitability | Best for small meals and low power needs | Best for frequent use and larger meals |
Understanding Microwave Wattage: Low vs High
Microwave wattage directly impacts cooking speed and energy efficiency, with low-watt microwaves typically ranging from 600 to 800 watts and high-watt microwaves from 900 to 1200 watts or more. High-watt microwaves consume more power but reduce cooking time, leading to potential energy savings during frequent use, whereas low-watt microwaves use less power overall but may require longer cooking cycles. Choosing between low and high wattage depends on balancing power consumption with cooking efficiency and household energy goals.
Power Consumption Differences in Low-Watt and High-Watt Microwaves
Low-watt microwaves, typically ranging from 600 to 900 watts, consume less power, making them ideal for energy-saving and small meal preparations. High-watt microwaves, often exceeding 1000 watts, use more electricity but provide faster cooking times and greater efficiency in heating. The power consumption difference significantly affects electricity bills, with low-watt models being more cost-effective for light use and high-watt units better suited for frequent, rapid cooking tasks.
Energy Efficiency: Which Microwave Wattage Saves More?
Low-watt microwaves consume less energy per use, making them ideal for small tasks and reducing overall electricity bills in low-frequency cooking scenarios. High-watt microwaves heat food faster but use more power per minute, which may result in similar or higher energy consumption depending on cooking duration. Selecting the appropriate wattage based on usage patterns maximizes energy efficiency and minimizes power waste.
Cooking Performance: Low-Watt vs High-Watt Microwaves
Low-watt microwaves, typically ranging from 600 to 800 watts, consume less power but often require longer cooking times and may struggle with dense or large meals, affecting overall cooking performance. High-watt microwaves, usually between 900 to 1200 watts, deliver faster and more even cooking by generating more intense heat, making them suitable for a wider variety of dishes. Choosing between low-watt and high-watt microwaves depends on balancing energy efficiency with the need for cooking speed and meal complexity.
Cost Implications of Microwave Wattage Choices
Low-watt microwaves consume less electricity, resulting in lower monthly energy bills but often require more cooking time, which can offset some savings. High-watt microwaves use more power, increasing immediate energy costs but reducing cooking duration and improving efficiency, potentially lowering overall power consumption during frequent use. Choosing the right wattage balances upfront energy expenses with long-term cost savings based on individual cooking habits and frequency.
Suitability for Small Kitchens: Low-Watt Microwaves
Low-watt microwaves typically consume between 600 to 900 watts, making them ideal for small kitchens where space and energy efficiency are priorities. These models offer sufficient power for basic reheating and light cooking tasks while reducing electricity usage and minimizing heat output. Compact designs of low-watt microwaves also fit easily into tight kitchen spaces, supporting energy-conscious living without sacrificing convenience.
High-Watt Microwaves: Speed and Power Benefits
High-watt microwaves, typically ranging from 1000 to 1500 watts, deliver faster cooking times and more consistent heat distribution compared to low-watt models. These microwaves enhance energy efficiency by reducing overall power consumption during use, despite their higher wattage rating. Consumers experience improved performance for reheating, defrosting, and cooking complex meals quickly, making high-watt microwaves ideal for busy kitchens.
Comparing Electricity Bills: Low-Watt vs High-Watt Microwaves
Low-watt microwaves consume between 600 to 800 watts, resulting in lower electricity usage and reduced monthly energy bills compared to high-watt microwaves that typically operate at 1000 to 1200 watts. Despite longer cooking times, low-watt models offer energy efficiency by using less power per minute, contributing to cost savings on electricity. High-watt microwaves deliver faster heating but increase power consumption, leading to higher electricity costs over time.
Selecting the Right Microwave Wattage for Your Needs
Low-watt microwaves, typically ranging from 600 to 900 watts, consume less power and are ideal for light cooking tasks or small households, offering energy-efficient operation. High-watt microwaves, usually between 1000 to 1200 watts or more, provide faster cooking times and are better suited for heavy usage or larger families, but they consume more electricity. Selecting the right microwave wattage depends on balancing cooking speed and energy consumption according to your specific needs and usage patterns.
Environmental Impact: Low-Watt and High-Watt Microwaves
Low-watt microwaves consume less electricity, reducing overall energy demand and lowering carbon emissions compared to high-watt models. High-watt microwaves operate faster but require more power, increasing environmental impact through higher energy use and greater greenhouse gas production. Choosing low-watt microwaves supports energy efficiency and sustainability by minimizing electricity consumption and contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
Low-Watt vs High-Watt Microwave for power consumption Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com