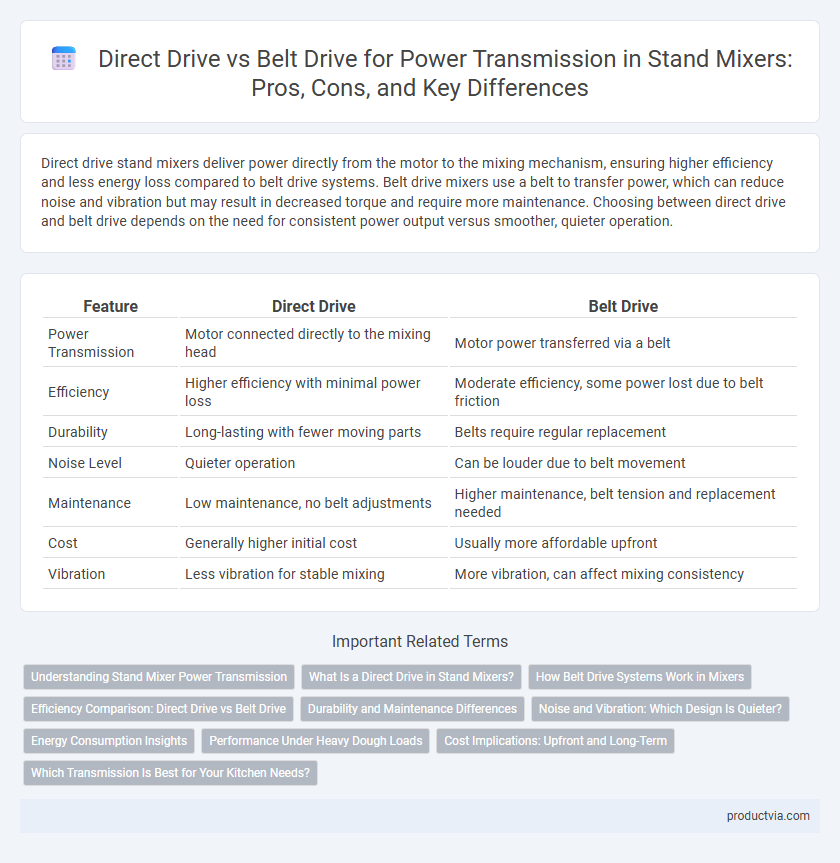
Direct drive stand mixers deliver power directly from the motor to the mixing mechanism, ensuring higher efficiency and less energy loss compared to belt drive systems. Belt drive mixers use a belt to transfer power, which can reduce noise and vibration but may result in decreased torque and require more maintenance. Choosing between direct drive and belt drive depends on the need for consistent power output versus smoother, quieter operation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Direct Drive | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | Motor connected directly to the mixing head | Motor power transferred via a belt |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency with minimal power loss | Moderate efficiency, some power lost due to belt friction |
| Durability | Long-lasting with fewer moving parts | Belts require regular replacement |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Can be louder due to belt movement |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no belt adjustments | Higher maintenance, belt tension and replacement needed |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Usually more affordable upfront |
| Vibration | Less vibration for stable mixing | More vibration, can affect mixing consistency |
Understanding Stand Mixer Power Transmission
Direct drive stand mixers transfer power directly from the motor to the mixing attachment, ensuring higher efficiency and durability with minimal power loss. Belt drive systems use a belt to connect the motor and attachment, providing quieter operation but often resulting in reduced torque and increased maintenance. Understanding these power transmission mechanisms helps users choose mixers based on performance, noise preference, and longevity requirements.
What Is a Direct Drive in Stand Mixers?
A direct drive in stand mixers means the motor is directly connected to the mixing attachment, providing more efficient power transmission and reduced energy loss compared to belt drive systems. This design offers improved durability and consistent torque, making it ideal for heavy-duty mixing tasks and dense doughs. Direct drive mixers typically require less maintenance and deliver quieter operation because there are no belts to wear out or slip during use.
How Belt Drive Systems Work in Mixers
Belt drive systems in stand mixers use a flexible belt wrapped around pulleys connected to the motor and the mixing mechanism, transferring power efficiently while minimizing noise and vibration. This setup allows the motor to operate at a different speed than the mixing attachment, providing smoother acceleration and better torque control during heavy mixing tasks. Belt drives are favored for their ability to absorb shocks and reduce wear on internal components, enhancing the mixer's durability and longevity.
Efficiency Comparison: Direct Drive vs Belt Drive
Direct drive stand mixers deliver power directly from the motor to the mixing mechanism, resulting in higher energy efficiency and less mechanical loss compared to belt drive systems. Belt drive mixers experience energy loss due to belt slippage and friction, which can reduce motor output and overall mixing power. Therefore, direct drive designs typically offer superior performance and consistency in power transmission for demanding kitchen tasks.
Durability and Maintenance Differences
Direct drive stand mixers offer enhanced durability due to the motor being directly connected to the mixing mechanism, reducing the number of moving parts and potential failure points. Belt drive mixers tend to require more frequent maintenance as the belt can wear out or slip, affecting performance and necessitating replacement. While direct drive systems generally provide longer-lasting power transmission with minimal upkeep, belt drive systems may offer quieter operation but at the cost of increased maintenance requirements.
Noise and Vibration: Which Design Is Quieter?
Direct drive stand mixers typically produce less noise and vibration because the motor is directly connected to the mixing mechanism, eliminating belt slippage and reducing mechanical friction. Belt drive mixers often generate more noise and vibration due to the belt's movement and potential alignment issues, which can cause additional mechanical stress and audible hums. Consequently, direct drive systems are generally considered quieter and smoother in operation, ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
Energy Consumption Insights
Direct drive stand mixers offer higher energy efficiency by transmitting power directly from the motor to the mixing mechanism, reducing energy loss. Belt drive models typically consume more power due to friction and slippage within the belt system, leading to decreased overall efficiency. For users prioritizing low energy consumption, direct drive mixers provide a more sustainable and cost-effective solution.
Performance Under Heavy Dough Loads
Direct drive stand mixers deliver superior performance under heavy dough loads due to their more efficient power transmission, enabling consistent torque and reduced power loss. Belt drive systems, while quieter and often less expensive, can experience slippage and decreased torque when handling dense or stiff mixtures. For tasks involving substantial kneading or thick doughs, direct drive mechanisms ensure enhanced durability and sustained mixing power.
Cost Implications: Upfront and Long-Term
Direct drive stand mixers typically have higher upfront costs due to their compact design and efficient power transmission, which reduces energy loss and enhances durability. Belt drive mixers often come with lower initial prices but may incur higher long-term maintenance expenses owing to belt replacements and potential slippage issues. Evaluating both options requires considering total cost of ownership, including repair frequency and energy efficiency.
Which Transmission Is Best for Your Kitchen Needs?
Direct drive stand mixers offer a more efficient power transfer with less energy loss, making them ideal for heavy-duty mixing tasks and long-term durability. Belt drive mixers provide quieter operation and smoother performance, better suited for everyday home baking and occasional use. Choosing the best transmission depends on your mixing frequency and the type of ingredients, with direct drive favored for intensive use and belt drive preferred for quieter, lighter workloads.
Direct drive vs belt drive for power transmission Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com