The pulse function in a food processor allows precise control over chopping and mixing by delivering short bursts of power, preventing over-processing and preserving texture. Continuous run mode maintains a steady, uninterrupted operation ideal for blending or pureeing ingredients smoothly and efficiently. Choosing between pulse and continuous run depends on the recipe's texture requirements and desired consistency.
Table of Comparison
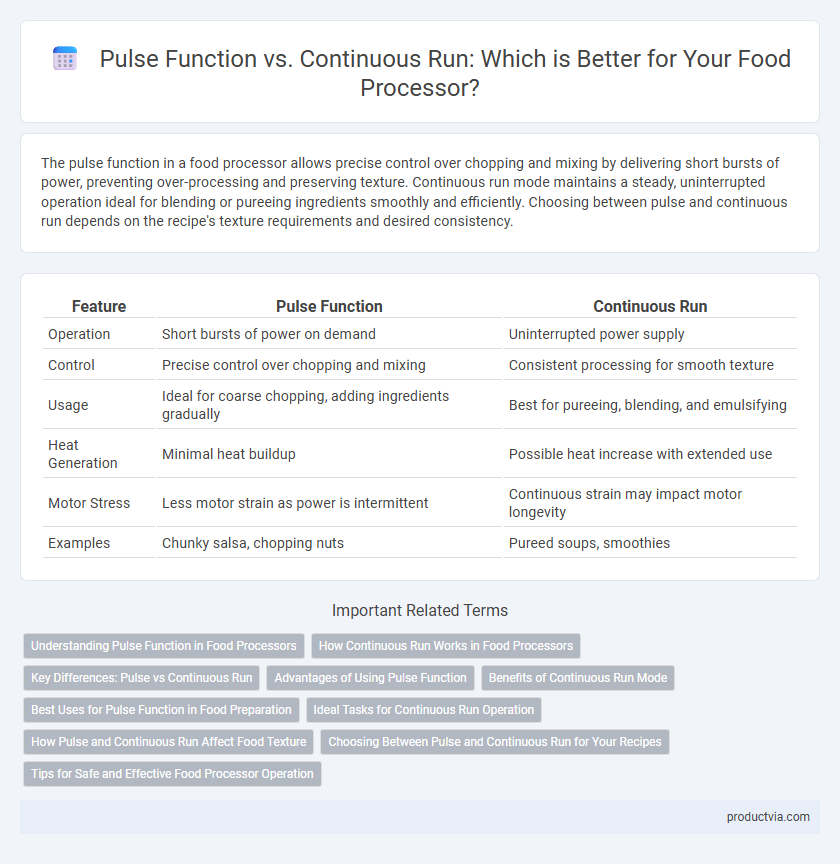
| Feature | Pulse Function | Continuous Run |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Short bursts of power on demand | Uninterrupted power supply |
| Control | Precise control over chopping and mixing | Consistent processing for smooth texture |
| Usage | Ideal for coarse chopping, adding ingredients gradually | Best for pureeing, blending, and emulsifying |
| Heat Generation | Minimal heat buildup | Possible heat increase with extended use |
| Motor Stress | Less motor strain as power is intermittent | Continuous strain may impact motor longevity |
| Examples | Chunky salsa, chopping nuts | Pureed soups, smoothies |
Understanding Pulse Function in Food Processors
The pulse function in food processors provides short bursts of power that allow for precise control over chopping, blending, or mixing, preventing over-processing of ingredients. Unlike continuous run, which operates at a consistent speed until stopped, the pulse function enables the user to achieve desired texture by manually timing the pulses. This mode is especially useful for tasks like chopping vegetables evenly or incorporating ingredients without turning them into a puree.
How Continuous Run Works in Food Processors
Continuous run in food processors operates by maintaining a steady motor speed to chop or blend ingredients uniformly, allowing for consistent texture and thorough mixing. This mode is ideal for tasks requiring extended processing like pureeing soups or kneading dough, providing uninterrupted power for smoother results. The continuous run mechanism utilizes a user-controlled start and stop, ensuring precise control over processing time and outcome.
Key Differences: Pulse vs Continuous Run
The Pulse function in a food processor delivers short, controlled bursts of power, allowing precise chopping and preventing over-processing, ideal for tasks like coarse chopping or mixing chunky ingredients. Continuous run mode operates at a steady speed for extended periods, suitable for blending or pureeing ingredients smoothly without interruption. Key differences include control level, processing consistency, and the ability to maintain texture, where pulse offers more versatility and continuous run ensures uniform results.
Advantages of Using Pulse Function
The pulse function in a food processor offers precise control over chopping, blending, and mixing by delivering short bursts of power, preventing over-processing of ingredients. It is ideal for tasks that require texture retention, such as coarsely chopping vegetables or kneading dough without overheating the motor. Using the pulse feature enhances consistency and preserves ingredient integrity, making it a versatile option compared to continuous run.
Benefits of Continuous Run Mode
Continuous run mode in a food processor enables efficient and consistent blending, making it ideal for large quantities or tougher ingredients. This mode maintains steady power, ensuring smooth textures and uniform chopping without interruption. It reduces manual effort and time compared to pulse function, enhancing overall food preparation speed.
Best Uses for Pulse Function in Food Preparation
The Pulse function in a food processor allows precise, controlled chopping and mixing by operating in short bursts, ideal for tasks requiring texture variation such as chopping nuts, making salsa, or crushing ice without overprocessing. It prevents ingredients from turning into a puree, which is crucial for recipes needing a coarse or chunky consistency. This function is essential for recipes where maintaining ingredient integrity and texture is paramount.
Ideal Tasks for Continuous Run Operation
Continuous run operation in a food processor is ideal for tasks requiring sustained power and consistency, such as making dough, pureeing soups, or mixing batters. It maintains a steady speed to ensure even processing and smooth textures, unlike the pulse function which delivers short bursts of power. This mode is essential for recipes needing prolonged blending to achieve uniform results.
How Pulse and Continuous Run Affect Food Texture
The Pulse function in a food processor delivers short bursts of power, allowing precise control over chopping and mixing, resulting in chunkier and more textured food. Continuous run mode blends ingredients uniformly with consistent power, producing smoother and finer textures ideal for purees and doughs. Choosing between pulse and continuous run directly influences the final food texture, enabling tailored preparation from coarse to silky consistency.
Choosing Between Pulse and Continuous Run for Your Recipes
Selecting the pulse function on a food processor offers precise control, allowing you to chop or mix ingredients in short bursts for a coarse or chunky texture. Continuous run mode is ideal for blending, pureeing, or processing large batches uniformly and quickly. Understanding when to use pulse for texture variety versus continuous run for smooth consistency enhances recipe outcomes and food preparation efficiency.
Tips for Safe and Effective Food Processor Operation
Using the pulse function in a food processor allows controlled, short bursts of power, preventing over-processing and preserving food texture. Continuous run should be limited to avoid motor overheating and ensure safe operation. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for maximum run time and allow cooling periods to maintain appliance longevity and performance.
Pulse function vs Continuous run for food processor Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com