Magnetic stainless steel is ideal for induction stoves due to its excellent magnetic properties and lightweight design, ensuring quick and even heating. Cast iron retains heat longer and offers superior durability but is heavier and may scratch the stove surface if not handled carefully. Choosing between the two depends on balancing heating performance with ease of use and maintenance for induction cooking.
Table of Comparison
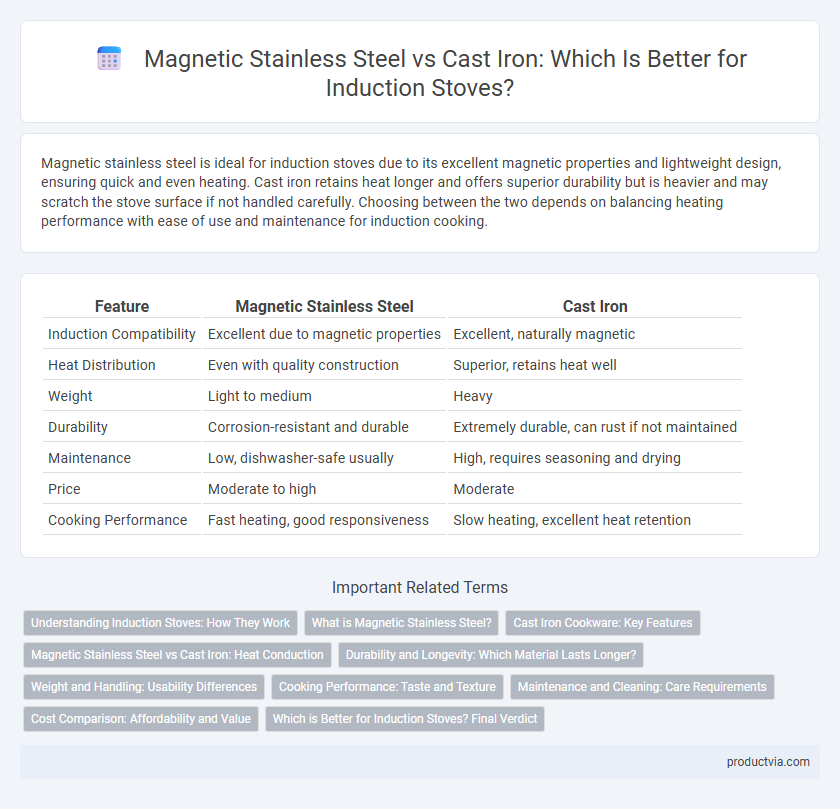
| Feature | Magnetic Stainless Steel | Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Compatibility | Excellent due to magnetic properties | Excellent, naturally magnetic |
| Heat Distribution | Even with quality construction | Superior, retains heat well |
| Weight | Light to medium | Heavy |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant and durable | Extremely durable, can rust if not maintained |
| Maintenance | Low, dishwasher-safe usually | High, requires seasoning and drying |
| Price | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Cooking Performance | Fast heating, good responsiveness | Slow heating, excellent heat retention |
Understanding Induction Stoves: How They Work
Magnetic stainless steel and cast iron both serve as effective cookware materials for induction stoves due to their ferromagnetic properties, essential for generating the electromagnetic field that heats the pan. Induction stoves rely on this magnetic interaction to produce heat directly within the cookware, making materials like cast iron and specific grades of magnetic stainless steel highly compatible. While cast iron offers superior magnetic permeability, magnetic stainless steel provides better corrosion resistance and lighter weight, influencing cookware performance and durability on induction cooktops.
What is Magnetic Stainless Steel?
Magnetic stainless steel is a type of stainless steel alloy specifically designed with a high iron content, making it responsive to the electromagnetic fields used in induction stoves. Unlike non-magnetic stainless steel, magnetic stainless steel contains ferritic or martensitic structures that allow efficient heat generation through induction cooking. Its durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with induction technology make it a popular material for cookware optimized for induction stoves.
Cast Iron Cookware: Key Features
Cast iron cookware offers excellent heat retention and even heating, making it ideal for induction stoves that require magnetic materials. Its durability and natural non-stick properties improve with use, enhancing cooking performance over time. Heavy weight and strong magnetism ensure consistent contact with the induction surface, optimizing energy efficiency.
Magnetic Stainless Steel vs Cast Iron: Heat Conduction
Magnetic stainless steel offers faster and more even heat conduction on induction stoves compared to cast iron, which heats more slowly and retains heat longer. Cast iron's high heat retention makes it ideal for steady, consistent cooking, while magnetic stainless steel's quick response enables precise temperature control. Both materials are compatible with induction technology, but stainless steel provides superior heat distribution for efficient cooking.
Durability and Longevity: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Magnetic stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains structural integrity over time, making it less prone to rust and wear under frequent induction stove use. Cast iron, while highly durable and able to withstand high heat, is susceptible to chipping and rust if not properly maintained. Overall, magnetic stainless steel typically lasts longer on induction stoves due to its enhanced resistance to environmental factors and routine wear.
Weight and Handling: Usability Differences
Magnetic stainless steel is lighter and easier to handle compared to cast iron, enhancing user comfort during cooking. Cast iron's heavier weight provides excellent heat retention but can be cumbersome to lift and maneuver on an induction stove. The choice between these materials affects usability, balancing portability and heat performance for induction cookware.
Cooking Performance: Taste and Texture
Magnetic stainless steel heats quickly and evenly on induction stoves, preserving the natural flavors and moisture of food for enhanced taste and texture. Cast iron retains heat longer, providing steady, consistent cooking that deepens flavors and creates rich textures, especially with slow-cooked dishes. Choosing between these materials impacts searing quality and heat distribution, directly influencing the final meal's taste and mouthfeel.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Care Requirements
Magnetic stainless steel cookware for induction stoves offers easy maintenance with its smooth, non-porous surface that resists rust and stains, enabling quick cleaning with mild detergents and a soft cloth. Cast iron requires more meticulous care, including thorough drying after washing to prevent rust, frequent seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface, and avoiding soap that can damage the seasoning layer. Proper maintenance of cast iron extends its lifespan, but magnetic stainless steel demands less effort and provides greater convenience for daily cleaning.
Cost Comparison: Affordability and Value
Magnetic stainless steel cookware generally offers greater affordability and versatility for induction stoves compared to cast iron, often costing 20-40% less while maintaining durability. Cast iron, though typically more expensive upfront due to its heavy construction and seasoning requirements, provides excellent heat retention and long-term value through longevity. Consumers prioritizing budget-friendly options will find magnetic stainless steel a more cost-effective choice without sacrificing induction compatibility.
Which is Better for Induction Stoves? Final Verdict
Magnetic stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and a lighter weight, making it easier to handle on induction stoves, while cast iron provides exceptional heat retention and even cooking performance. For induction cooking, magnetic stainless steel is often preferred due to its quick response to temperature changes and compatibility with induction technology, although cast iron's durability and ability to maintain steady heat make it valuable for slow cooking. The final verdict favors magnetic stainless steel for everyday use on induction stoves, while cast iron remains ideal for specialized cooking requiring consistent heat.
Magnetic stainless steel vs cast iron for induction stove Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com