Centrifugal juicers work quickly by using high-speed spinning blades to extract juice, but they generate heat that can reduce nutrient content and shelf life. Masticating juicers operate at slower speeds, gently crushing fruits and vegetables to preserve enzymes and yield cold-pressed juice with higher nutrient retention. For those prioritizing maximum juice quality and longevity, masticating juicers offer a superior cold-pressed juice experience compared to centrifugal models.
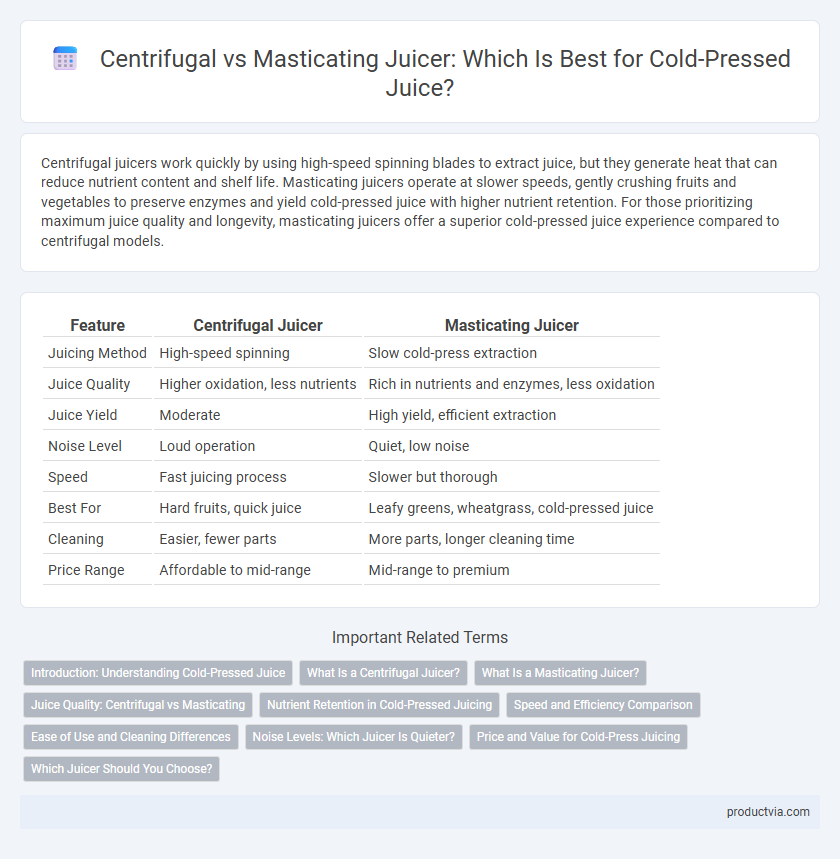
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Centrifugal Juicer | Masticating Juicer |
|---|---|---|
| Juicing Method | High-speed spinning | Slow cold-press extraction |
| Juice Quality | Higher oxidation, less nutrients | Rich in nutrients and enzymes, less oxidation |
| Juice Yield | Moderate | High yield, efficient extraction |
| Noise Level | Loud operation | Quiet, low noise |
| Speed | Fast juicing process | Slower but thorough |
| Best For | Hard fruits, quick juice | Leafy greens, wheatgrass, cold-pressed juice |
| Cleaning | Easier, fewer parts | More parts, longer cleaning time |
| Price Range | Affordable to mid-range | Mid-range to premium |
Introduction: Understanding Cold-Pressed Juice
Cold-pressed juice is extracted using low-speed, high-pressure methods that preserve nutrients and enzymes, distinguishing it from high-speed centrifugal juicing. Masticating juicers operate at slower RPMs, minimizing heat and oxidation, which helps retain the juice's nutritional quality. In contrast, centrifugal juicers use fast-spinning blades that generate heat, potentially compromising the cold-pressed juice's freshness and nutrient density.
What Is a Centrifugal Juicer?
A centrifugal juicer operates by rapidly spinning a metal blade against a juicing mesh, separating juice from pulp through centrifugal force. This type of juicer is known for its fast processing time and ability to handle a variety of fruits and vegetables, but it generates heat and exposes juice to air, which can reduce nutrient retention compared to cold-pressed methods. While centrifugal juicers are convenient for quick juicing, they typically produce juice with less shelf life and lower nutrient density than masticating juicers.
What Is a Masticating Juicer?
A masticating juicer, also known as a cold-press juicer, operates by slowly crushing and pressing fruits and vegetables to extract juice, preserving maximum nutrients and enzymes. This method generates less heat and oxidation compared to centrifugal juicers, resulting in higher quality, longer-lasting juice with richer flavor. Ideal for leafy greens and wheatgrass, masticating juicers produce a smoother, nutrient-dense juice that retains more vitamins and antioxidants.
Juice Quality: Centrifugal vs Masticating
Masticating juicers extract juice through slow, cold-pressing, preserving more nutrients, enzymes, and antioxidants compared to centrifugal juicers, which use high-speed spinning and generate heat that can degrade juice quality. Cold-pressed juice from masticating juicers typically has higher vitamin retention, richer flavor, and longer shelf life. Centrifugal juicers are faster but often produce juice with more foam, oxidation, and lower nutrient density.
Nutrient Retention in Cold-Pressed Juicing
Masticating juicers excel in nutrient retention for cold-pressed juice due to their slow extraction process, which minimizes heat and oxidation. Centrifugal juicers, while faster, generate more heat and expose juice to air, leading to nutrient degradation and reduced enzyme activity. For optimal preservation of vitamins, antioxidants, and enzymes, masticating juicers are the preferred choice in cold-pressed juicing.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Centrifugal juicers operate at high speeds, quickly extracting juice by spinning fruits and vegetables against a mesh filter, making them ideal for fast juice preparation. Masticating juicers use a slow, grinding process that preserves more nutrients and yields higher-quality cold-pressed juice but takes longer to complete. Efficiency-wise, masticating juicers produce more juice per ingredient and minimize oxidation, whereas centrifugal juicers sacrifice some juice quality for speed.
Ease of Use and Cleaning Differences
Centrifugal juicers operate at high speeds, making them easier to use for quick juice extraction but often produce more foam and oxidation, reducing juice freshness. Masticating juicers work at slower speeds with an auger mechanism, resulting in higher juice quality and longer shelf life, though they require more effort to assemble and clean. Cleaning centrifugal models typically involves fewer parts and less time, whereas masticating juicers have more components that demand thorough rinsing to maintain hygiene and performance.
Noise Levels: Which Juicer Is Quieter?
Masticating juicers operate at slower speeds, producing significantly less noise, typically around 40-60 decibels, compared to centrifugal juicers that run at higher speeds and generate noise levels between 80-100 decibels. The lower noise output of masticating juicers makes them ideal for quiet environments and early morning juicing without disturbing others. Centrifugal juicers, while faster, have louder motor and blade operations, often sounding like a blender or food processor.
Price and Value for Cold-Press Juicing
Centrifugal juicers generally offer a lower upfront cost, making them accessible for budget-conscious consumers seeking quick juicing solutions. Masticating juicers, despite being pricier, provide higher extraction efficiency and better nutrient retention, delivering superior cold-pressed juice quality and long-term value. Evaluating price against cold-pressed juice benefits, masticating juicers present a more economical investment for health-focused users prioritizing maximum juice yield and nutrient preservation.
Which Juicer Should You Choose?
Centrifugal juicers extract juice quickly using high-speed spinning blades but generate heat that may reduce nutrient retention, making them less ideal for cold-pressed juice. Masticating juicers operate at low speeds by crushing and slowly pressing fruits and vegetables, preserving enzymes and nutrients critical for high-quality cold-pressed juice. Choose a masticating juicer for maximum nutrient preservation and better juice yield if cold-pressed quality is your priority.
Centrifugal juicer vs masticating juicer for cold-pressed juice Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com