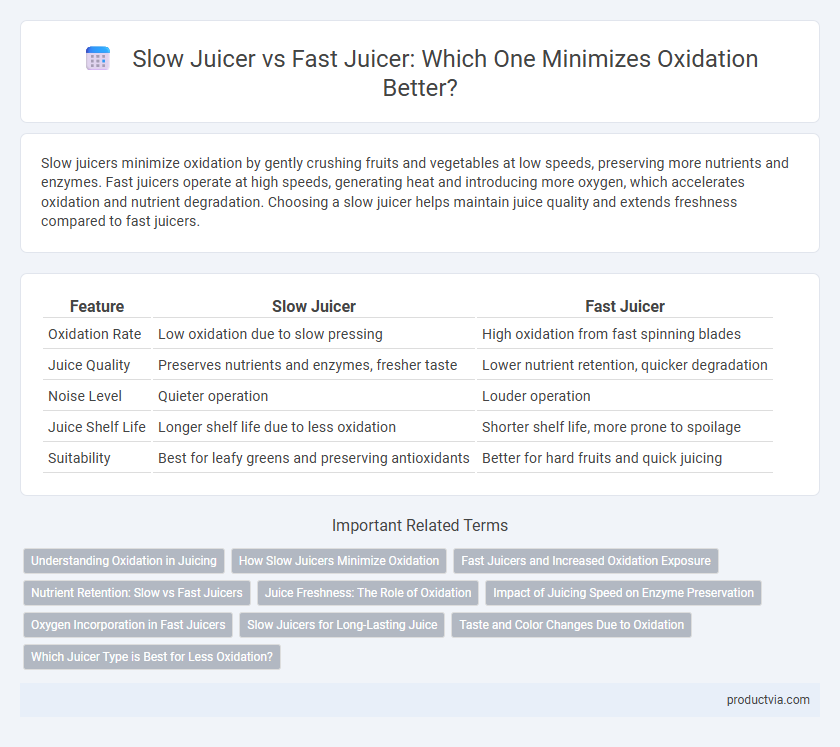
Slow juicers minimize oxidation by gently crushing fruits and vegetables at low speeds, preserving more nutrients and enzymes. Fast juicers operate at high speeds, generating heat and introducing more oxygen, which accelerates oxidation and nutrient degradation. Choosing a slow juicer helps maintain juice quality and extends freshness compared to fast juicers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Slow Juicer | Fast Juicer |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Rate | Low oxidation due to slow pressing | High oxidation from fast spinning blades |
| Juice Quality | Preserves nutrients and enzymes, fresher taste | Lower nutrient retention, quicker degradation |
| Noise Level | Quieter operation | Louder operation |
| Juice Shelf Life | Longer shelf life due to less oxidation | Shorter shelf life, more prone to spoilage |
| Suitability | Best for leafy greens and preserving antioxidants | Better for hard fruits and quick juicing |
Understanding Oxidation in Juicing
Slow juicers minimize oxidation by gently crushing fruits and vegetables at low speeds, preserving nutrients and enzymes more effectively than fast juicers. Fast juicers operate at high speeds, generating heat and introducing more air, which accelerates oxidation and nutrient degradation. Understanding oxidation's impact on juice freshness and nutrient retention helps consumers choose slow juicers for higher quality, longer-lasting juice.
How Slow Juicers Minimize Oxidation
Slow juicers minimize oxidation by operating at low speeds, typically between 40 to 80 RPM, which reduces heat buildup and limits air exposure during the extraction process. The gentle masticating action preserves enzymes and nutrients by preventing the rapid agitation that introduces oxygen, resulting in juice with longer shelf life and improved antioxidant retention. This method contrasts with fast juicers, whose high-speed spinning promotes oxidation, leading to quicker nutrient degradation.
Fast Juicers and Increased Oxidation Exposure
Fast juicers operate at high speeds, which causes increased oxidation due to greater exposure of juice to air during the extraction process. This oxidation accelerates nutrient degradation, reducing the antioxidant content and freshness of the juice. Compared to slow juicers, fast juicers produce juice that typically has a shorter shelf life and diminished health benefits because of the elevated oxidation levels.
Nutrient Retention: Slow vs Fast Juicers
Slow juicers operate at low speeds, minimizing oxidation and preserving higher levels of nutrients such as enzymes, vitamins, and antioxidants during the extraction process. Fast juicers generate heat and incorporate more air through rapid spinning, leading to increased oxidation which can degrade sensitive nutrients and reduce overall juice quality. Studies indicate slow juicers retain up to 40% more nutrients compared to fast juicers, making them a superior choice for maximum nutrient retention.
Juice Freshness: The Role of Oxidation
Slow juicers minimize oxidation by gently crushing and pressing fruits and vegetables, preserving more nutrients and extending juice freshness up to 72 hours. Fast juicers operate at high speeds, generating heat and incorporating more air, which accelerates oxidation and leads to quicker nutrient degradation and juice spoilage within hours. Choosing a slow juicer significantly improves juice quality by reducing enzymatic browning and maintaining vibrant color and flavor longer.
Impact of Juicing Speed on Enzyme Preservation
Slow juicers operate at low speeds, minimizing heat generation and oxidation, which preserves delicate enzymes and nutrients in the juice. In contrast, fast juicers spin rapidly, increasing oxidation and heat exposure that can degrade enzyme activity and reduce nutritional value. Choosing slow juicers ensures higher retention of enzymes essential for digestion and health benefits.
Oxygen Incorporation in Fast Juicers
Fast juicers rapidly spin blades at high speeds, causing significant oxygen incorporation that accelerates oxidation, leading to quicker nutrient degradation in juice. Slow juicers operate at low speeds, minimizing oxygen exposure and preserving antioxidants, vitamins, and enzymes for longer-lasting freshness. The reduced oxidation in slow juicers results in juice with higher nutrient retention and better flavor stability compared to fast juicers.
Slow Juicers for Long-Lasting Juice
Slow juicers operate at lower RPMs, minimizing oxidation and preserving the juice's nutritional content for a longer time compared to fast juicers. The gentle cold-press extraction method used in slow juicing reduces heat buildup, preventing nutrient degradation and maintaining fresher-tasting juice. As a result, juice from slow juicers can stay fresh for up to 72 hours without significant loss of vitamins and antioxidants.
Taste and Color Changes Due to Oxidation
Slow juicers minimize oxidation by extracting juice at lower speeds, preserving more natural flavors and vibrant color, resulting in a fresher taste and richer appearance. Fast juicers operate at higher speeds, introducing more air into the juice, which accelerates oxidation and can lead to faster browning and a slightly altered, less fresh taste. The reduced oxidation in slow juicers helps maintain the juice's nutrient content, color stability, and overall sensory quality longer compared to fast juicers.
Which Juicer Type is Best for Less Oxidation?
Slow juicers operate at lower speeds, minimizing heat and air exposure, which significantly reduces oxidation and preserves more nutrients and enzymes. Fast juicers, or centrifugal juicers, spin at high speeds, introducing more oxygen that accelerates oxidation, leading to quicker nutrient degradation. For those prioritizing freshness and longer-lasting juice quality, slow juicers are the optimal choice to minimize oxidation effects.
Slow juicer vs Fast juicer for oxidation Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com