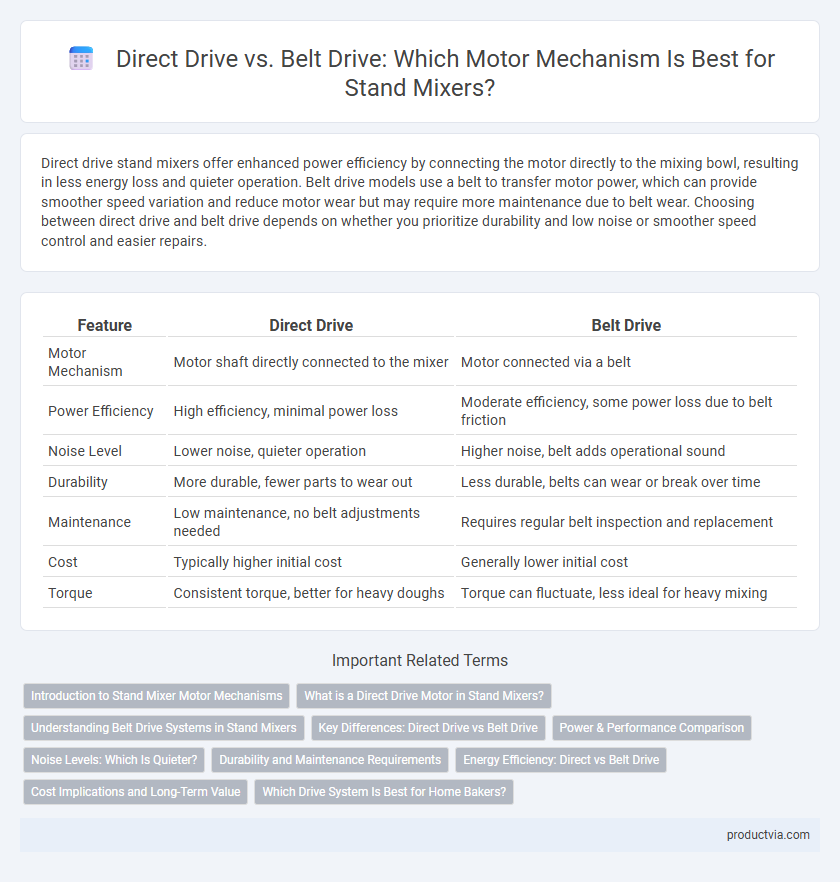
Direct drive stand mixers offer enhanced power efficiency by connecting the motor directly to the mixing bowl, resulting in less energy loss and quieter operation. Belt drive models use a belt to transfer motor power, which can provide smoother speed variation and reduce motor wear but may require more maintenance due to belt wear. Choosing between direct drive and belt drive depends on whether you prioritize durability and low noise or smoother speed control and easier repairs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Direct Drive | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Mechanism | Motor shaft directly connected to the mixer | Motor connected via a belt |
| Power Efficiency | High efficiency, minimal power loss | Moderate efficiency, some power loss due to belt friction |
| Noise Level | Lower noise, quieter operation | Higher noise, belt adds operational sound |
| Durability | More durable, fewer parts to wear out | Less durable, belts can wear or break over time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no belt adjustments needed | Requires regular belt inspection and replacement |
| Cost | Typically higher initial cost | Generally lower initial cost |
| Torque | Consistent torque, better for heavy doughs | Torque can fluctuate, less ideal for heavy mixing |
Introduction to Stand Mixer Motor Mechanisms
Stand mixers feature two primary motor mechanisms: direct drive and belt drive, each influencing performance and durability. Direct drive motors connect the motor shaft directly to the mixer, offering higher torque and efficiency with less maintenance. Belt drive systems use a belt to transfer power, providing quieter operation but potentially requiring more frequent adjustments and wear over time.
What is a Direct Drive Motor in Stand Mixers?
A direct drive motor in stand mixers connects the motor shaft directly to the mixing attachment, providing efficient power transfer and reduced energy loss. This mechanism ensures quieter operation and enhanced durability compared to belt-driven models, which rely on a belt to transfer motor power. Direct drive motors deliver consistent torque and are preferred for heavy-duty mixing tasks due to their robust and reliable design.
Understanding Belt Drive Systems in Stand Mixers
Belt drive systems in stand mixers use a flexible belt connected to the motor pulley, allowing smooth transmission of power to the mixing attachment while reducing motor noise and vibration. This mechanism provides shock absorption during heavy mixing tasks, enhancing durability and preventing motor strain. Understanding the belt drive's ability to deliver consistent torque at varying speeds helps users choose mixers suited for diverse baking needs.
Key Differences: Direct Drive vs Belt Drive
Direct drive stand mixers connect the motor directly to the mixing mechanism, offering higher efficiency, greater power, and reduced motor noise. Belt drive mixers use a belt to transfer power from the motor to the mixing mechanism, providing smoother operation with less vibration and typically quieter performance. Key differences include maintenance requirements, with belts needing occasional replacement, and torque delivery, where direct drive systems generally offer stronger, more consistent torque for heavy-duty mixing tasks.
Power & Performance Comparison
Direct drive stand mixer motors are mounted directly onto the mixing attachment, ensuring maximum power transfer and consistent speed under heavy loads, ideal for handling dense doughs and large batches. Belt drive models use a belt and pulley system that offers quieter operation and smoother acceleration but may experience power loss or slipping under high-torque conditions, reducing overall performance. For tasks requiring sustained high power and durability, direct drive mixers outperform belt drive counterparts in torque retention and reliable performance.
Noise Levels: Which Is Quieter?
Direct drive stand mixers produce less noise due to the motor being directly connected to the mixing mechanism, reducing vibrations and mechanical friction. Belt drive mixers generate higher noise levels because the belt transfers motor power, causing more movement and potential slippage during operation. Noise measurements show direct drive models typically operate around 50-60 decibels, while belt drive mixers often exceed 65 decibels under similar conditions.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Direct drive stand mixers feature motors connected directly to the mixing mechanism, resulting in greater durability and less frequent maintenance due to fewer moving parts and reduced wear. Belt drive mixers use a belt to transfer power from the motor to the mixing head, which can lead to increased maintenance needs as belts wear out and require replacement over time. For long-term reliability and lower upkeep, direct drive models are generally favored, especially in professional or heavy-use environments.
Energy Efficiency: Direct vs Belt Drive
Direct drive stand mixers offer superior energy efficiency by transferring power directly from the motor to the mixing mechanism, reducing energy loss typically caused by belt friction. Belt drive systems experience higher energy consumption as belts can slip or stretch, leading to less efficient motor performance and increased wear over time. Choosing a direct drive model enhances durability while minimizing electricity usage, making it an optimal choice for energy-conscious users.
Cost Implications and Long-Term Value
Direct drive stand mixers typically have a higher upfront cost due to their advanced motor mechanism, which connects the motor directly to the mixing attachment, resulting in enhanced efficiency and durability. Belt drive mixers generally cost less initially but may incur higher maintenance expenses over time due to belt wear and replacement needs. Investing in a direct drive model offers greater long-term value through consistent performance and reduced repair costs.
Which Drive System Is Best for Home Bakers?
Direct drive systems in stand mixers offer superior motor efficiency and greater power transfer, making them ideal for home bakers tackling heavy doughs or large batches. Belt drive mixers provide quieter operation and absorb motor vibrations better, which benefits users prioritizing noise reduction and smoother performance. Home bakers seeking durability and high torque often prefer direct drive models, while those valuing quieter, lighter tasks may opt for belt drive mixers.
Direct drive vs Belt drive for motor mechanism Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com