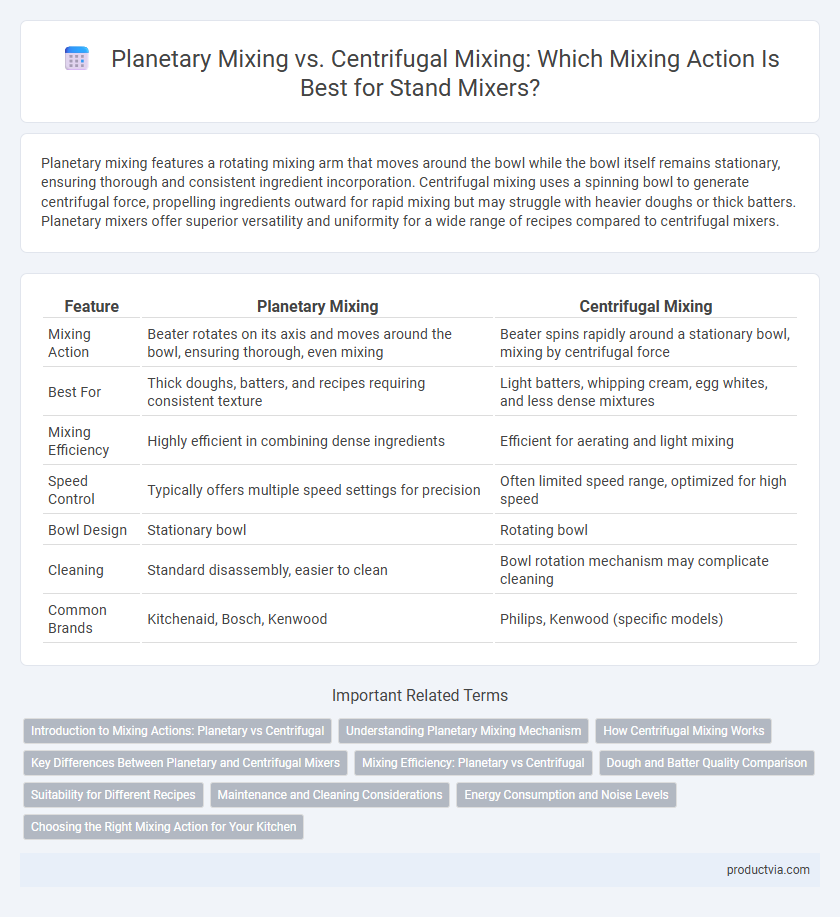
Planetary mixing features a rotating mixing arm that moves around the bowl while the bowl itself remains stationary, ensuring thorough and consistent ingredient incorporation. Centrifugal mixing uses a spinning bowl to generate centrifugal force, propelling ingredients outward for rapid mixing but may struggle with heavier doughs or thick batters. Planetary mixers offer superior versatility and uniformity for a wide range of recipes compared to centrifugal mixers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Planetary Mixing | Centrifugal Mixing |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing Action | Beater rotates on its axis and moves around the bowl, ensuring thorough, even mixing | Beater spins rapidly around a stationary bowl, mixing by centrifugal force |
| Best For | Thick doughs, batters, and recipes requiring consistent texture | Light batters, whipping cream, egg whites, and less dense mixtures |
| Mixing Efficiency | Highly efficient in combining dense ingredients | Efficient for aerating and light mixing |
| Speed Control | Typically offers multiple speed settings for precision | Often limited speed range, optimized for high speed |
| Bowl Design | Stationary bowl | Rotating bowl |
| Cleaning | Standard disassembly, easier to clean | Bowl rotation mechanism may complicate cleaning |
| Common Brands | Kitchenaid, Bosch, Kenwood | Philips, Kenwood (specific models) |
Introduction to Mixing Actions: Planetary vs Centrifugal
Planetary mixing involves a beater rotating on its axis while simultaneously revolving around the bowl, ensuring thorough ingredient incorporation and consistent texture. Centrifugal mixing uses a spinning bowl with stationary beaters, leveraging centrifugal force to push ingredients outward for rapid mixing in thin batter applications. Each method suits different mixing requirements, with planetary mixers excelling in heavy doughs and centrifugal mixers preferred for lighter batters and creams.
Understanding Planetary Mixing Mechanism
Planetary mixing involves a mixing attachment that rotates on its own axis while simultaneously orbiting around the bowl, ensuring thorough and consistent ingredient incorporation. This dual motion targets all areas of the bowl, reducing unmixed pockets and achieving a homogeneous blend. In contrast, centrifugal mixing relies primarily on high-speed spinning, which may result in uneven mixing for dense or complex mixtures.
How Centrifugal Mixing Works
Centrifugal mixing operates by spinning the mixing bowl at high speeds while stationary blades rotate independently, creating a powerful outward force that pushes ingredients against the bowl walls for effective blending. This method is highly efficient for whipping and mixing liquid or semi-liquid ingredients due to the rapid motion generating strong shear forces. Unlike planetary mixing, centrifugal mixers excel in tasks requiring quick incorporation of air, making them ideal for batters and creams.
Key Differences Between Planetary and Centrifugal Mixers
Planetary mixers feature a mixing blade that rotates on its axis while simultaneously moving around the bowl, ensuring thorough and consistent ingredient incorporation ideal for thick or dense batters. Centrifugal mixers use a spinning bowl with stationary beaters, relying on centrifugal force to push ingredients outward, making them better suited for light batters and fast mixing tasks. Key differences include the planetary mixer's versatility with various dough types and the centrifugal mixer's efficiency in handling quick, high-speed mixing of less viscous mixtures.
Mixing Efficiency: Planetary vs Centrifugal
Planetary mixing offers superior mixing efficiency by utilizing dual rotational motion, enabling thorough ingredient incorporation and consistent batter texture. Centrifugal mixing relies on a high-speed spinning bowl that forces ingredients outward, often resulting in less uniform blends and requiring longer mixing times. For dense doughs and complex recipes, planetary mixers provide reliable, even mixing that reduces preparation time and improves final product quality.
Dough and Batter Quality Comparison
Planetary mixing delivers thorough and consistent dough development by rotating the beater around the bowl's circumference, ensuring uniform gluten formation and optimal batter aeration. Centrifugal mixing uses high-speed spinning to create a swift mixing motion, which can lead to overworking dough and uneven batter texture, reducing quality in delicate recipes. For superior dough elasticity and smooth, homogeneous batter, planetary mixers provide enhanced control and precision in mixing action.
Suitability for Different Recipes
Planetary mixing offers a thorough and consistent blend by rotating the beater around the bowl while the bowl itself spins, making it ideal for dense doughs, batters, and mixtures requiring intensive mixing such as bread and cake recipes. Centrifugal mixing relies on high-speed rotating blades that force ingredients against the bowl walls and suits lighter mixtures like whipped cream, sauces, and quick batters for pancakes or muffins. Choosing between planetary and centrifugal mixing depends on recipe texture and mixing intensity, favoring planetary mixers for robust doughs and centrifugal mixers for delicate or fast-prep mixtures.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Planetary mixers utilize a rotating mixing action along with an orbital motion of the beater, which can create intricate parts prone to food buildup, requiring thorough cleaning to prevent residue accumulation. Centrifugal mixers rely on a spinning bowl and stationary beaters, often featuring simpler designs that facilitate easier disassembly and cleaning with fewer hard-to-reach areas. Maintenance of planetary mixers may involve more frequent inspection of gears and seals due to complex mechanics, whereas centrifugal mixers typically benefit from straightforward upkeep and reduced risk of mechanical wear.
Energy Consumption and Noise Levels
Planetary mixers use a dual-motion mechanism that ensures consistent and thorough mixing with moderate energy consumption and lower noise levels, ideal for precision tasks in home and professional kitchens. Centrifugal mixers operate by spinning the bowl rapidly, which results in higher energy usage and louder noise output due to increased motor strain and friction. Choosing between the two depends on the balance of desired energy efficiency and acceptable noise thresholds in the mixing environment.
Choosing the Right Mixing Action for Your Kitchen
Planetary mixing offers thorough and consistent mixing by rotating the beater on its axis while simultaneously orbiting the bowl, ideal for thick doughs and batters. Centrifugal mixing spins the bowl rapidly while stationary beaters rely on centrifugal force to push ingredients outward, best suited for lightweight mixtures like whipped cream or egg whites. Selecting the right mixing action depends on your typical recipes and desired texture, where planetary mixers excel in versatility and centrifugal mixers provide speed for lighter ingredients.
Planetary mixing vs Centrifugal mixing for mixing action Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com