Deep freeze preserves food by lowering temperatures gradually, allowing for stable and long-term storage with minimal cellular damage. Quick freeze rapidly reduces temperature, creating smaller ice crystals that better maintain food texture and nutritional value. Choosing between deep freeze and quick freeze depends on the type of food and desired quality retention during storage.
Table of Comparison
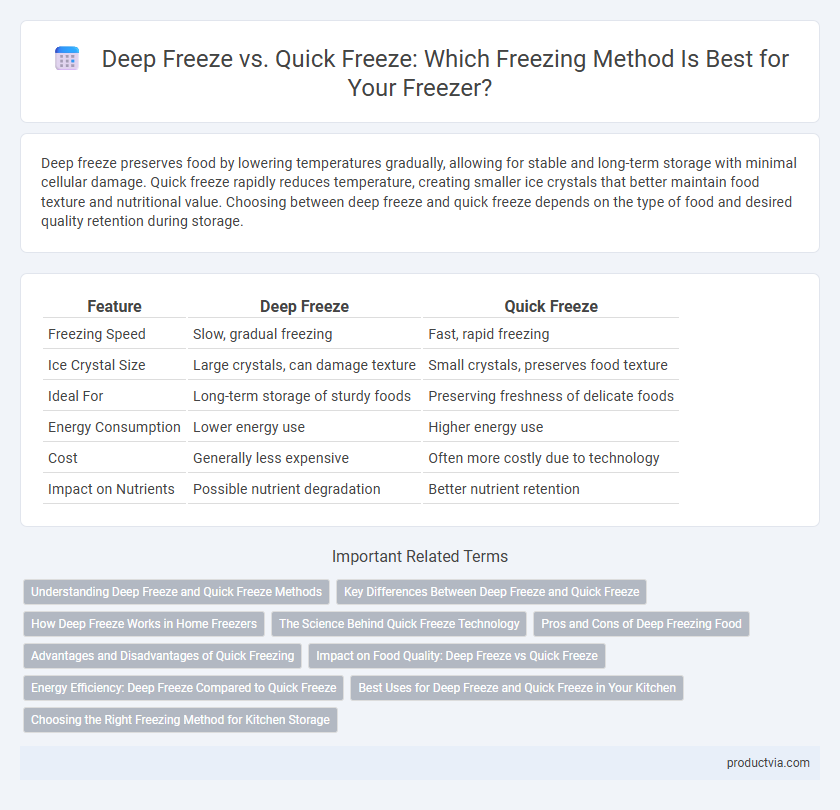
| Feature | Deep Freeze | Quick Freeze |
|---|---|---|
| Freezing Speed | Slow, gradual freezing | Fast, rapid freezing |
| Ice Crystal Size | Large crystals, can damage texture | Small crystals, preserves food texture |
| Ideal For | Long-term storage of sturdy foods | Preserving freshness of delicate foods |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy use | Higher energy use |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Often more costly due to technology |
| Impact on Nutrients | Possible nutrient degradation | Better nutrient retention |
Understanding Deep Freeze and Quick Freeze Methods
Deep freeze method preserves food by maintaining temperatures well below freezing point, typically around -18degC or lower, ensuring long-term quality retention by slowing enzyme activity and microbial growth. Quick freeze method rapidly lowers the temperature of food to around -30degC, minimizing ice crystal formation and preserving cellular structure for better texture and taste upon thawing. Both methods are essential in food preservation, with deep freeze suited for prolonged storage and quick freeze optimal for maintaining fresh-like qualities.
Key Differences Between Deep Freeze and Quick Freeze
Deep freeze preserves food by maintaining extremely low temperatures, typically below -18degC, causing slow ice crystal formation that minimizes cellular damage for long-term storage. Quick freeze operates at even colder temperatures, often below -30degC, rapidly freezing food to create smaller ice crystals that better retain texture, flavor, and nutritional value. The key difference lies in freezing speed and temperature, with quick freeze offering superior preservation quality, especially for delicate or perishable items.
How Deep Freeze Works in Home Freezers
Deep freeze in home freezers maintains a consistently low temperature, typically around -18degC (0degF), to preserve food by slowing enzymatic activity and microbial growth over long periods. This process involves removing heat gradually from the food, allowing ice crystals to form slowly within cells, which helps retain texture and nutritional value. Unlike quick freeze methods that freeze food rapidly at much lower temperatures, deep freeze ensures stable storage conditions without the need for specialized equipment.
The Science Behind Quick Freeze Technology
Quick freeze technology utilizes ultra-low temperatures and rapid air circulation to freeze food items swiftly, preserving cellular structure and minimizing ice crystal formation. This process contrasts with traditional deep freeze methods, which lower temperature gradually, often leading to larger ice crystals and potential texture degradation. Rapid freezing ensures better retention of nutrients, flavor, and overall food quality by limiting cellular damage during the freezing cycle.
Pros and Cons of Deep Freezing Food
Deep freezing food preserves nutritional value and texture by rapidly lowering the temperature to -18degC or below, preventing large ice crystals from forming and minimizing cell damage. This method offers long-term storage benefits but may consume more energy and take longer to freeze compared to quick freezing, which cools food faster but can cause uneven freezing and texture changes. Deep freezing is ideal for maintaining quality in meat, fruits, and vegetables over extended periods despite higher operational costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quick Freezing
Quick freezing preserves food quality by rapidly lowering temperature, minimizing ice crystal formation and cellular damage, which retains texture and nutrients better than slower methods. However, it requires specialized equipment and higher energy consumption, leading to increased operational costs. The rapid process may sometimes cause surface dehydration or freezer burn if not properly managed.
Impact on Food Quality: Deep Freeze vs Quick Freeze
Quick freeze preserves food texture and nutrients more effectively by rapidly reducing temperature and minimizing ice crystal formation, which prevents cell damage. Deep freeze uses slower freezing rates that can lead to larger ice crystals, causing moisture loss and altered texture upon thawing. Choosing quick freeze methods enhances flavor retention and overall food quality during long-term storage.
Energy Efficiency: Deep Freeze Compared to Quick Freeze
Deep freeze technology consumes significantly less energy than quick freeze methods by maintaining consistently low temperatures without frequent temperature fluctuations. Quick freeze requires intense bursts of energy to rapidly lower product temperature, resulting in higher electricity consumption. Energy-efficient deep freeze systems leverage optimized insulation and steady-state cooling to reduce overall power usage during long-term storage.
Best Uses for Deep Freeze and Quick Freeze in Your Kitchen
Deep freeze methods are ideal for long-term storage of large quantities of meat, seafood, and ready-to-eat meals, preserving texture and nutritional value by maintaining consistently low temperatures. Quick freeze techniques rapidly lower the temperature of delicate items like fruits, vegetables, and baked goods, preventing ice crystal formation and preserving freshness and flavor. Choosing deep freeze for bulk storage and quick freeze for fresh produce ensures optimal food quality and reduces waste in your kitchen.
Choosing the Right Freezing Method for Kitchen Storage
Deep freeze technology maintains ultra-low temperatures around -30degC to -40degC, preserving food quality for extended periods by minimizing ice crystal formation. Quick freeze operates at slightly higher temperatures, typically between -18degC and -25degC, rapidly freezing food to lock in moisture and texture. Selecting between deep freeze and quick freeze depends on storage duration and food type, with deep freeze ideal for long-term preservation and quick freeze suited for maintaining freshness in short-term kitchen storage.
Deep freeze vs Quick freeze for freezing method Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com