Cookware compatibility with induction stoves depends primarily on the magnetic properties of the pot or pan, requiring materials like cast iron or stainless steel for proper functionality. Heat distribution varies significantly among compatible cookware, with thicker bases generally providing more even heating, preventing hotspots that can affect cooking quality. Selecting induction-compatible cookware that balances magnetic responsiveness with effective heat conduction ensures efficient cooking performance and energy savings.
Table of Comparison
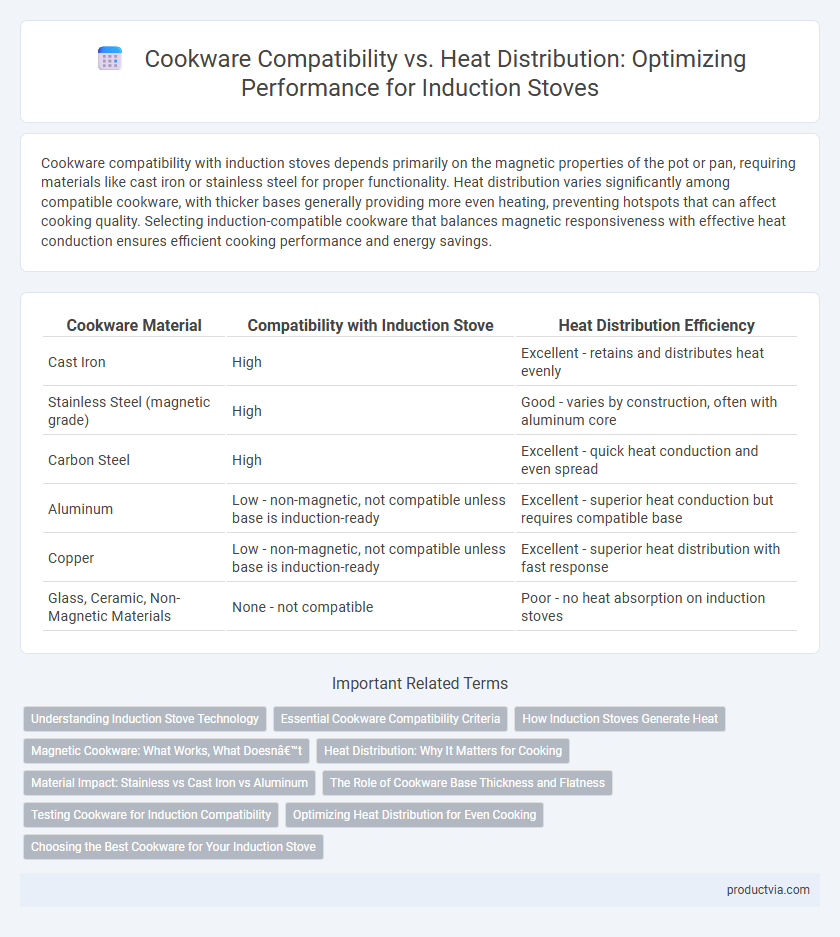
| Cookware Material | Compatibility with Induction Stove | Heat Distribution Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | High | Excellent - retains and distributes heat evenly |
| Stainless Steel (magnetic grade) | High | Good - varies by construction, often with aluminum core |
| Carbon Steel | High | Excellent - quick heat conduction and even spread |
| Aluminum | Low - non-magnetic, not compatible unless base is induction-ready | Excellent - superior heat conduction but requires compatible base |
| Copper | Low - non-magnetic, not compatible unless base is induction-ready | Excellent - superior heat distribution with fast response |
| Glass, Ceramic, Non-Magnetic Materials | None - not compatible | Poor - no heat absorption on induction stoves |
Understanding Induction Stove Technology
Cookware compatibility for induction stoves hinges on magnetic properties, requiring materials like cast iron or stainless steel with ferrous bases to activate the electromagnetic field. Heat distribution efficiency depends on the cookware's flatness and metal composition, ensuring uniform contact and rapid energy transfer. Understanding induction stove technology reveals that the induction coil generates an alternating magnetic field, producing heat directly in compatible cookware for precise and energy-efficient cooking.
Essential Cookware Compatibility Criteria
Essential cookware compatibility criteria for induction stoves include the presence of magnetic properties in the cookware base, ensuring it can interact effectively with the induction cooktop's magnetic field. Cookware made from materials like cast iron, magnetic stainless steel, and certain multi-ply pans provide optimal heat distribution while maintaining compatibility. Proper base flatness and thickness also influence efficient heat transfer and uniform cooking performance on induction stoves.
How Induction Stoves Generate Heat
Induction stoves generate heat through electromagnetic fields that directly heat compatible cookware made of ferromagnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel. Cookware with flat, smooth bottoms ensures optimal contact and efficient heat transfer, enhancing even heat distribution during cooking. Using incompatible cookware results in poor heat generation and uneven cooking performance.
Magnetic Cookware: What Works, What Doesn’t
Magnetic cookware made from ferrous metals such as cast iron and stainless steel with magnetic properties works best on induction stoves, enabling efficient heat transfer through electromagnetic fields. Non-magnetic materials like aluminum, copper, and glass do not generate the magnetic currents needed, causing uneven heat distribution or no heating at all. Using cookware with a flat, smooth bottom ensures optimal contact with the induction surface, maximizing both compatibility and consistent heat spread.
Heat Distribution: Why It Matters for Cooking
Heat distribution on induction stoves is crucial because it ensures even cooking by transferring energy directly to compatible cookware materials such as ferrous metals. Cookware with a magnetic base, like cast iron or stainless steel, consistently spreads heat across the cooking surface, preventing hot spots and promoting uniform temperature. Poor heat distribution leads to uneven cooking, affecting food texture and flavor, making the choice of cookware pivotal for induction stove performance.
Material Impact: Stainless vs Cast Iron vs Aluminum
Stainless steel cookware offers moderate heat distribution and excellent induction compatibility due to its magnetic properties, making it a popular choice for induction stoves. Cast iron provides superior heat retention and even distribution, enhancing cooking performance on induction surfaces but is heavier and requires careful maintenance. Aluminum, while excellent in heat conduction, is typically incompatible with induction cooktops unless fitted with a magnetic base, balancing lightweight convenience with necessary functionality.
The Role of Cookware Base Thickness and Flatness
Cookware base thickness and flatness significantly impact heat distribution on an induction stove, as a thicker and flatter base ensures more efficient magnetic coupling and uniform heat transfer. Thin or uneven bases can cause hotspots and reduce energy efficiency, leading to inconsistent cooking results. Optimal cookware for induction stoves features a flat, heavy-duty base made from ferromagnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel with a magnetic layer.
Testing Cookware for Induction Compatibility
Testing cookware for induction compatibility involves checking for magnetic properties, as only ferromagnetic materials like cast iron and certain stainless steels work efficiently on induction stoves. Cookware with uneven or non-magnetic bases can cause poor heat distribution, leading to hotspots and inconsistent cooking results. Using a magnet test or manufacturer specifications ensures optimal performance and even heating on induction cooktops.
Optimizing Heat Distribution for Even Cooking
Selecting cookware with a flat, magnetic base made of materials like cast iron or stainless steel significantly enhances heat distribution on induction stoves, promoting even cooking. Cookware that closely matches the induction cooktop's size ensures efficient electromagnetic energy transfer, reducing hot spots and improving temperature consistency. Optimizing these factors leads to precise heat control and uniform food preparation across the cooking surface.
Choosing the Best Cookware for Your Induction Stove
Selecting cookware with magnetic properties, such as cast iron or stainless steel, ensures optimal compatibility with induction stoves, promoting efficient heat transfer. Even heat distribution is crucial to prevent hotspots and enhance cooking performance, making flat-bottomed pans ideal for this purpose. Prioritizing cookware specifically designed for induction maximizes energy efficiency and cooking precision.
Cookware compatibility vs heat distribution for induction stove Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com