Plug-in induction cooktops offer easy installation and mobility, allowing users to connect the stove directly to a standard electrical outlet without complex wiring. Hardwired induction units require professional installation, providing a more secure and permanent power connection that can handle higher wattage for consistent performance. Choosing between plug-in and hardwired options depends on kitchen setup, power requirements, and user preference for flexibility versus durability.
Table of Comparison
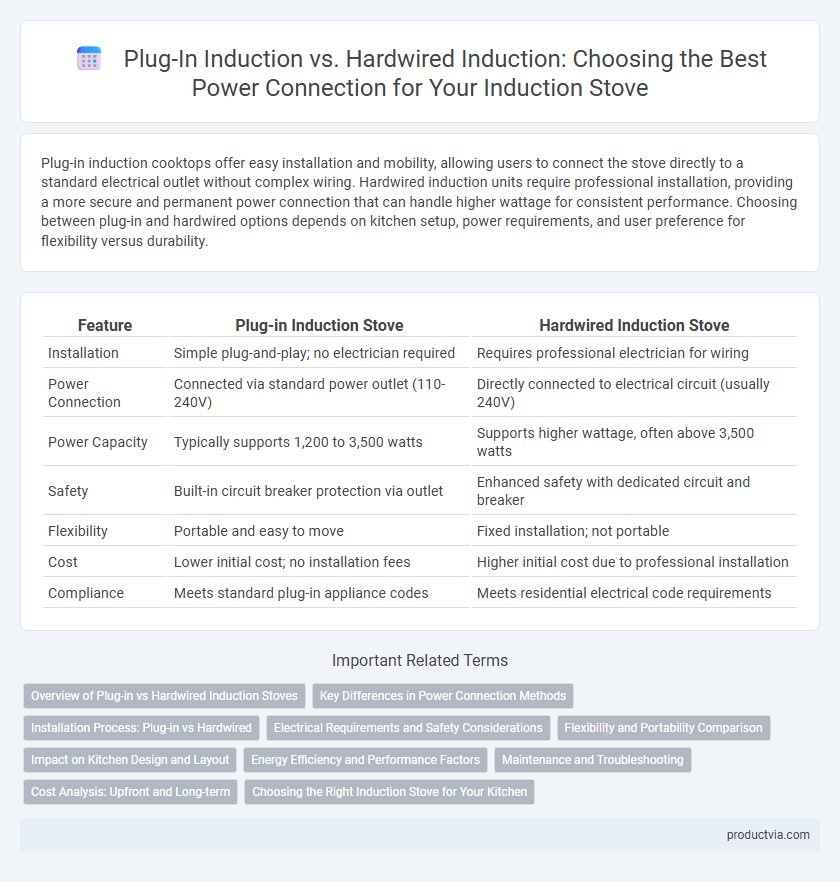
| Feature | Plug-in Induction Stove | Hardwired Induction Stove |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Simple plug-and-play; no electrician required | Requires professional electrician for wiring |
| Power Connection | Connected via standard power outlet (110-240V) | Directly connected to electrical circuit (usually 240V) |
| Power Capacity | Typically supports 1,200 to 3,500 watts | Supports higher wattage, often above 3,500 watts |
| Safety | Built-in circuit breaker protection via outlet | Enhanced safety with dedicated circuit and breaker |
| Flexibility | Portable and easy to move | Fixed installation; not portable |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; no installation fees | Higher initial cost due to professional installation |
| Compliance | Meets standard plug-in appliance codes | Meets residential electrical code requirements |
Overview of Plug-in vs Hardwired Induction Stoves
Plug-in induction stoves offer flexibility with easy installation, making them ideal for renters or temporary setups, whereas hardwired induction stoves provide a permanent, more secure power connection suitable for high-power cooking appliances. Plug-in models typically connect to standard electrical outlets with lower amperage requirements, while hardwired units require professional installation to handle higher voltage and amperage, ensuring consistent performance. Choosing between plug-in and hardwired options depends on kitchen infrastructure, cooking needs, and electrical capacity.
Key Differences in Power Connection Methods
Plug-in induction stoves connect to a standard electrical outlet, allowing easy installation and portability, typically supporting lower power limits around 120V or 240V. Hardwired induction stoves require a direct electrical connection to the circuit breaker, enabling higher wattage capacities suitable for heavy-duty cooking with stable power delivery. The plug-in method offers convenience and flexibility, whereas hardwired connections provide superior performance and safety for high-power cooking environments.
Installation Process: Plug-in vs Hardwired
Plug-in induction stoves offer a straightforward installation process by connecting directly to a standard electrical outlet, making them ideal for DIY setups and temporary use. Hardwired induction stoves require professional installation, involving permanent connection to the home's electrical system, ensuring a more secure and reliable power supply. The choice between plug-in and hardwired significantly impacts installation time, cost, and compatibility with existing kitchen wiring.
Electrical Requirements and Safety Considerations
Plug-in induction stoves typically operate on standard 120-volt outlets, making installation simpler but often limiting power output and cooking performance compared to hardwired models. Hardwired induction stoves require a dedicated 240-volt circuit, ensuring higher power capacity for faster heating and more consistent temperature control, essential for heavy-duty cooking. From a safety perspective, hardwired connections reduce the risk of loose plugs or accidental disconnections, while plug-in models must adhere to strict outlet standards to prevent electrical hazards and overloads.
Flexibility and Portability Comparison
Plug-in induction stoves offer superior flexibility and portability by allowing easy connection and disconnection from standard electrical outlets, making them ideal for temporary setups and frequent relocations. Hardwired induction stoves require professional installation directly into the electrical system, providing a more permanent, stable power connection but limiting mobility. The plug-in option suits users seeking versatile kitchen arrangements, while hardwired models are preferred for fixed installations with consistent power demands.
Impact on Kitchen Design and Layout
Plug-in induction stoves offer flexibility in kitchen design, allowing easier repositioning and reducing the need for dedicated electrical wiring, which suits dynamic layouts. Hardwired induction units require fixed installation, optimizing space utilization by eliminating visible cords and enabling seamless integration into custom cabinetry. Choosing between plug-in and hardwired impacts countertop continuity, appliance placement, and overall aesthetic cohesion in modern kitchen designs.
Energy Efficiency and Performance Factors
Plug-in induction stoves offer flexible installation and ease of use but may face limitations in power capacity, affecting peak performance and energy efficiency compared to hardwired models. Hardwired induction stoves provide a direct electrical connection that supports higher wattage, resulting in faster heating times and more consistent energy consumption. Energy efficiency is maximized with hardwired systems due to stable power delivery, minimizing energy loss and enhancing overall cooking performance.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Plug-in induction stoves offer easier maintenance and troubleshooting due to their simple detachable connections, allowing quick replacement or repair without electrical work. Hardwired induction units require professional service for troubleshooting, as their fixed installations involve direct wiring to the electrical system. The plug-in design reduces downtime and service complexity, while hardwired models provide a more secure, permanent connection but pose higher repair complexity.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term
Plug-in induction stoves typically have lower upfront costs due to simpler installation, while hardwired induction systems require professional wiring, increasing initial expenses. Over the long term, plug-in models may incur higher maintenance or replacement costs if the plug or outlet fails, whereas hardwired systems offer greater durability and potentially lower ongoing costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership should consider installation fees, appliance lifespan, and potential electrical upgrades.
Choosing the Right Induction Stove for Your Kitchen
Plug-in induction stoves offer ease of installation and portability, making them ideal for renters or temporary setups, typically requiring standard 120V outlets. Hardwired induction stoves connect directly to the electrical system, supporting higher wattage and providing more consistent power output, suitable for built-in kitchen designs with 240V circuits. Selecting between plug-in and hardwired options depends on your kitchen's electrical capacity, desired stove power, and installation flexibility.
Plug-in induction vs Hardwired induction for power connection Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com