Electric popcorn makers rely on traditional electrical heating elements, providing consistent and quick heating suitable for most home kitchens. Induction popcorn makers use magnetic fields to heat the cooking vessel directly, resulting in faster, more energy-efficient cooking with precise temperature control. The choice between the two depends on kitchen compatibility and preferences for energy efficiency and heat management.
Table of Comparison
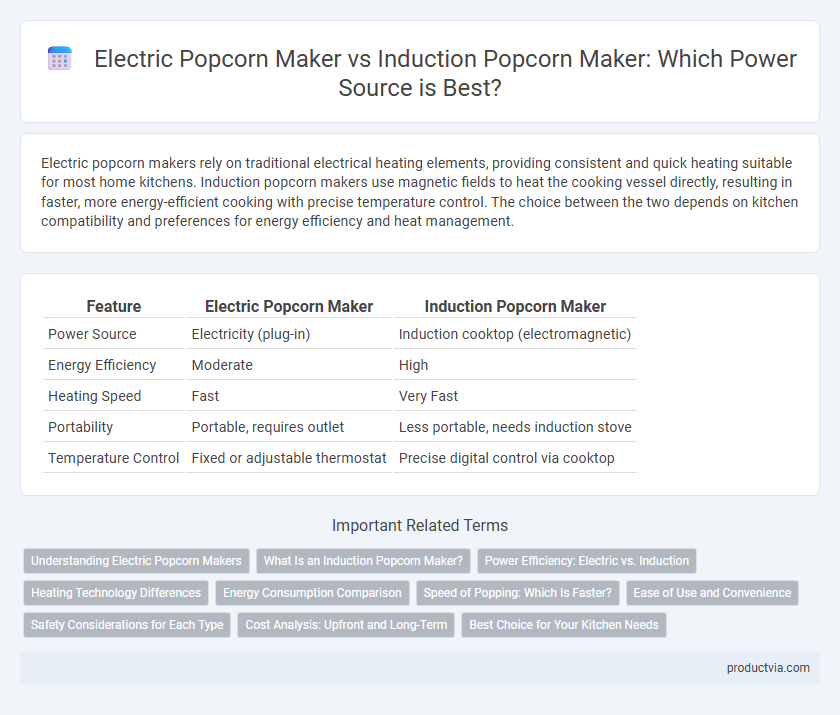
| Feature | Electric Popcorn Maker | Induction Popcorn Maker |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electricity (plug-in) | Induction cooktop (electromagnetic) |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Heating Speed | Fast | Very Fast |
| Portability | Portable, requires outlet | Less portable, needs induction stove |
| Temperature Control | Fixed or adjustable thermostat | Precise digital control via cooktop |
Understanding Electric Popcorn Makers
Electric popcorn makers use a direct electrical heating element to pop kernels quickly and efficiently, providing consistent heat control for even popping. In contrast, induction popcorn makers rely on electromagnetic fields to heat the cooking vessel, offering faster heating with improved energy efficiency but requiring compatible cookware. Understanding the direct power usage and heating mechanisms of electric popcorn makers helps consumers choose the best device for their convenience and popping performance.
What Is an Induction Popcorn Maker?
An induction popcorn maker uses electromagnetic fields to directly heat the cooking surface, offering precise temperature control and energy efficiency compared to traditional electric popcorn makers that rely on resistive heating elements. This method ensures rapid, even heating which prevents burning and delivers consistent popcorn quality. Induction technology reduces power consumption while maintaining high performance, making it an eco-friendly alternative for popcorn preparation.
Power Efficiency: Electric vs. Induction
Electric popcorn makers typically consume more power due to resistive heating elements that convert electricity directly into heat, resulting in moderate efficiency levels around 70-80%. Induction popcorn makers use electromagnetic fields to heat the popcorn vessel directly, achieving higher power efficiency close to 85-90%. The focused and rapid heating in induction models reduces energy waste, making them more energy-efficient compared to conventional electric popcorn machines.
Heating Technology Differences
Electric popcorn makers use traditional resistive heating elements that directly convert electrical energy into heat, providing consistent temperature control ideal for even popcorn popping. Induction popcorn makers employ electromagnetic fields to heat the cooking vessel itself, resulting in faster heat-up times and more energy-efficient performance. This difference in heating technology affects the overall speed, energy consumption, and temperature precision of the popcorn-making process.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Electric popcorn makers typically consume between 400 to 1200 watts, providing consistent heat for popping corn efficiently. Induction popcorn makers use electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the pot, often resulting in lower overall energy consumption due to faster heating times and minimal heat loss. Comparing energy consumption, induction models generally outperform traditional electric counterparts by converting energy more effectively, leading to reduced electricity usage per popping session.
Speed of Popping: Which Is Faster?
Electric popcorn makers typically use a direct heating element that rapidly heats the oil and kernels, resulting in popping times as fast as 3 to 5 minutes. Induction popcorn makers rely on electromagnetic fields to heat the pot itself, offering more efficient heat transfer but generally requiring a slightly longer time, around 5 to 7 minutes. The faster speed of electric popcorn makers makes them ideal for quick snacks, while induction models provide consistent heat distribution with a bit more patience.
Ease of Use and Convenience
Electric popcorn makers offer plug-and-play convenience with consistent power delivery, allowing users to start popping with minimal setup. Induction popcorn makers require compatible induction cooktops, which may limit portability but provide precise heat control for even popping. The electric models generally excel in ease of use due to their standalone design and straightforward operation.
Safety Considerations for Each Type
Electric popcorn makers operate on standard electrical outlets and often feature built-in thermal cutoffs to prevent overheating, reducing fire hazards during use. Induction popcorn makers use electromagnetic fields for heating, which can provide more precise temperature control and cooler external surfaces, minimizing burn risks. Both types require adherence to manufacturer safety guidelines, but induction models generally offer enhanced safety due to reduced direct heating elements and rapid shutoff capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Electric popcorn makers typically have a lower upfront cost, ranging from $20 to $50, but may incur higher long-term electricity expenses due to continuous power consumption. Induction popcorn makers often require an initial investment between $50 and $150, reflecting their advanced technology and efficient energy use, which translates to reduced electricity bills over time. Considering power source efficiency, induction models offer better cost savings in the long run despite a higher initial price.
Best Choice for Your Kitchen Needs
Electric popcorn makers operate using standard electrical outlets, offering consistent and easy-to-use power for home kitchens. Induction popcorn makers require induction-compatible cooktops, leveraging electromagnetic fields for faster and more energy-efficient heating. Choosing between them depends on your kitchen setup and energy preferences, with electric models being more universally accessible and induction models excelling in energy efficiency and temperature control.
Electric popcorn maker vs induction popcorn maker for power source Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com