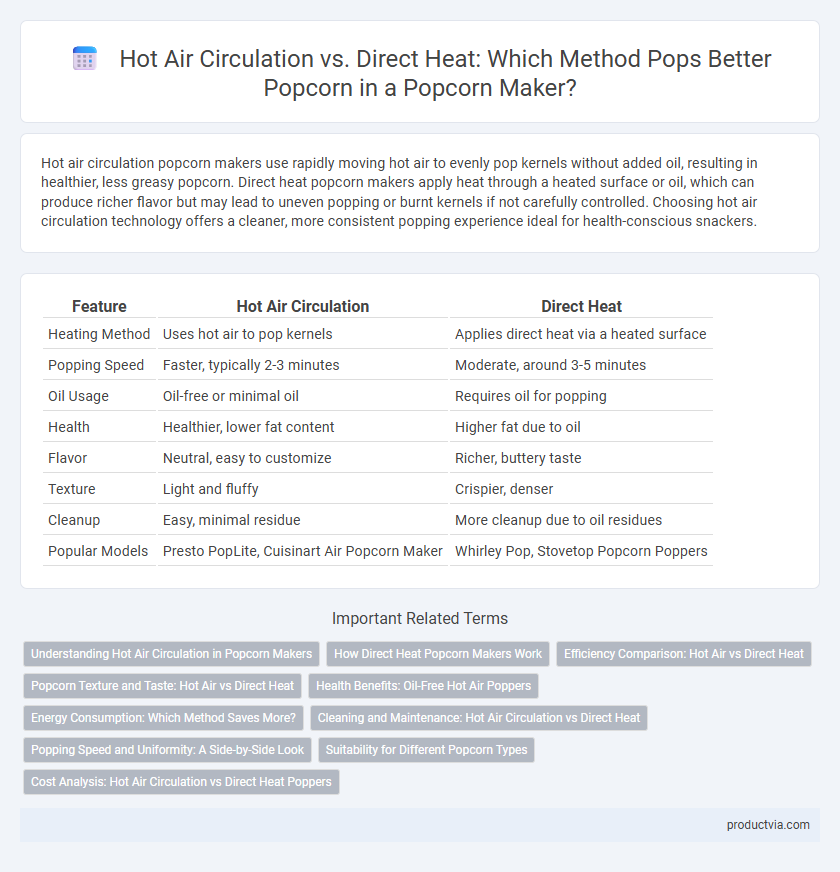
Hot air circulation popcorn makers use rapidly moving hot air to evenly pop kernels without added oil, resulting in healthier, less greasy popcorn. Direct heat popcorn makers apply heat through a heated surface or oil, which can produce richer flavor but may lead to uneven popping or burnt kernels if not carefully controlled. Choosing hot air circulation technology offers a cleaner, more consistent popping experience ideal for health-conscious snackers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Air Circulation | Direct Heat |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Uses hot air to pop kernels | Applies direct heat via a heated surface |
| Popping Speed | Faster, typically 2-3 minutes | Moderate, around 3-5 minutes |
| Oil Usage | Oil-free or minimal oil | Requires oil for popping |
| Health | Healthier, lower fat content | Higher fat due to oil |
| Flavor | Neutral, easy to customize | Richer, buttery taste |
| Texture | Light and fluffy | Crispier, denser |
| Cleanup | Easy, minimal residue | More cleanup due to oil residues |
| Popular Models | Presto PopLite, Cuisinart Air Popcorn Maker | Whirley Pop, Stovetop Popcorn Poppers |
Understanding Hot Air Circulation in Popcorn Makers
Hot air circulation in popcorn makers uses a powerful fan to evenly distribute heated air around the kernels, ensuring consistent popping and reducing the chance of burning. This method relies on convection heat, which minimizes oil usage and produces a lighter, healthier snack compared to direct heat techniques. Understanding this process highlights the benefits of even temperature control and enhanced popcorn quality in hot air poppers.
How Direct Heat Popcorn Makers Work
Direct heat popcorn makers operate by applying intense heat directly to the popcorn kernels, typically through a heated surface or oil bath, which causes the moisture inside the kernels to rapidly vaporize and create pressure until the kernels pop. This method often produces a richer flavor and a crispier texture due to the direct contact with heat and oil, enhancing the caramelization process on the popped corn. However, direct heat machines require careful temperature control to prevent burning and ensure even popping, making them popular in traditional stovetop or commercial popcorn machines.
Efficiency Comparison: Hot Air vs Direct Heat
Hot air circulation in popcorn makers ensures more uniform heating by evenly distributing heat around the kernels, significantly reducing the risk of burning and increasing popping efficiency. Direct heat methods apply high temperatures to the base, which can lead to uneven heating and a higher likelihood of unpopped kernels or burnt popcorn. As a result, hot air circulation models typically deliver faster popping times and better yield, optimizing both energy use and popcorn quality.
Popcorn Texture and Taste: Hot Air vs Direct Heat
Hot air circulation popcorn makers produce lighter, fluffier kernels with a consistent texture and reduced risk of burning, enhancing the natural popcorn flavor without added oil. Direct heat popcorn makers often yield richer, slightly crispier popcorn with a caramelized taste due to oil contact and higher cooking temperatures. The choice between hot air and direct heat impacts both the mouthfeel and flavor intensity, catering to preferences for either a healthier or more indulgent snack experience.
Health Benefits: Oil-Free Hot Air Poppers
Hot air circulation popcorn makers use rapid hot air to pop kernels without oil, significantly reducing fat and calorie intake compared to direct heat methods that often require added oil. Oil-free hot air poppers minimize exposure to unhealthy fats and cholesterol, promoting heart health and aiding weight management. This method also reduces the formation of harmful compounds that can occur with overheated oils, making it a healthier choice for everyday snacking.
Energy Consumption: Which Method Saves More?
Hot air circulation popcorn makers use convection to evenly pop kernels with minimal energy by circulating hot air, making them more energy-efficient than direct heat methods. Direct heat popcorn makers require more energy to maintain high temperatures and risk uneven popping, wasting both kernels and power. Studies show hot air circulation can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional stovetop or oil-based popping techniques.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Hot Air Circulation vs Direct Heat
Hot air circulation popcorn makers generally require less cleaning and maintenance since they use air to pop kernels, reducing oil residue buildup inside the machine. Direct heat models often accumulate more grease and burnt kernels, necessitating more frequent and thorough cleaning of the heating surfaces to prevent smoke and unpleasant odors. Regular maintenance is essential for both types to ensure optimal performance and longevity, but hot air models provide a cleaner popping experience with minimal cleanup effort.
Popping Speed and Uniformity: A Side-by-Side Look
Hot air circulation popcorn makers provide faster popping speeds by evenly distributing heat, ensuring most kernels pop simultaneously. Direct heat models often result in uneven popping, with some kernels burning while others remain unpopped due to hot spots. The uniform heat distribution in hot air poppers enhances overall popping efficiency and reduces burnt or partially popped kernels.
Suitability for Different Popcorn Types
Hot air circulation popcorn makers are ideal for popping classic, low-oil popcorn varieties, ensuring even heat distribution without burning kernels. Direct heat appliances excel with specialty or gourmet popcorn types, such as caramel or cheese-coated kernels, by providing consistent high temperatures for proper coating adhesion. Choosing between hot air and direct heat depends on the popcorn type, desired texture, and flavor intensity.
Cost Analysis: Hot Air Circulation vs Direct Heat Poppers
Hot air circulation popcorn makers typically consume more electricity due to longer cooking times but offer lower maintenance costs compared to direct heat poppers, which rely on heating elements that can wear out faster and may require more frequent replacement. Direct heat machines, often powered by stovetop or electric heating plates, tend to have lower upfront costs but can increase operational expenses due to uneven heating and burnt kernels leading to waste. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that hot air circulation poppers provide better efficiency and longevity, offsetting their higher initial investment with reduced energy consumption and maintenance over time.
Hot air circulation vs direct heat for popcorn popping Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com