Induction stoves require different voltage inputs based on their power needs, with 120V models typically sufficient for smaller, portable units, while 240V stoves deliver higher power output suitable for larger, more efficient cooking. The choice between 120V and 240V affects heat generation speed and overall energy consumption, with 240V stoves enabling faster cooking times and better performance. Ensuring your kitchen wiring matches the stove's voltage requirement is essential for safety and optimal functionality.
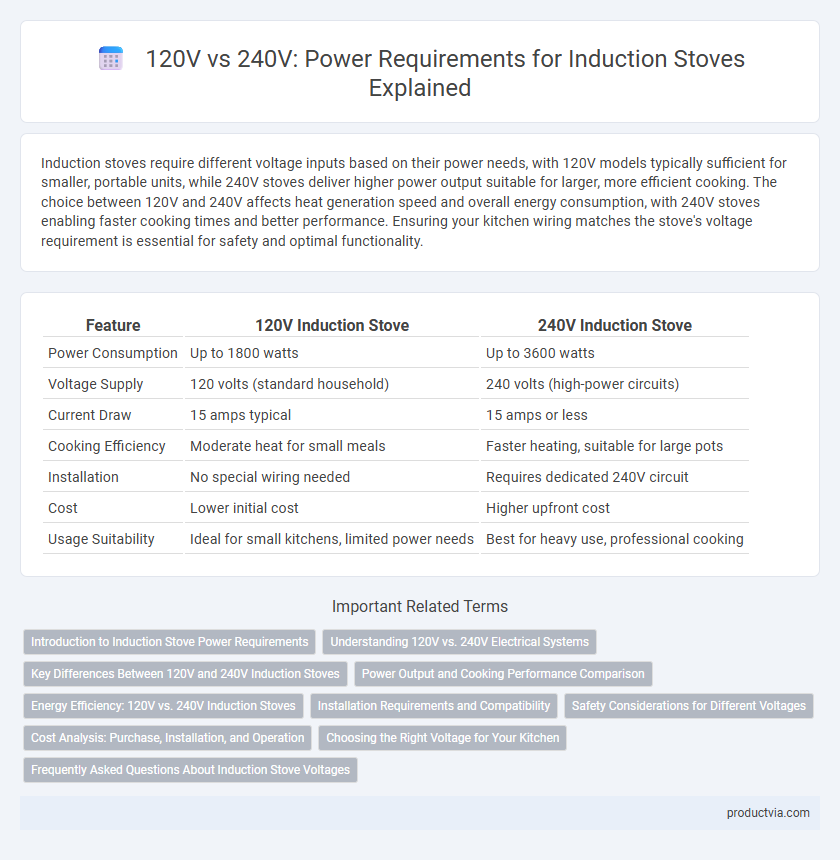
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 120V Induction Stove | 240V Induction Stove |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | Up to 1800 watts | Up to 3600 watts |
| Voltage Supply | 120 volts (standard household) | 240 volts (high-power circuits) |
| Current Draw | 15 amps typical | 15 amps or less |
| Cooking Efficiency | Moderate heat for small meals | Faster heating, suitable for large pots |
| Installation | No special wiring needed | Requires dedicated 240V circuit |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Usage Suitability | Ideal for small kitchens, limited power needs | Best for heavy use, professional cooking |
Introduction to Induction Stove Power Requirements
Induction stoves typically require a 120V or 240V power supply, with 240V models providing higher wattage for faster and more efficient cooking. A 120V induction stove usually offers between 1,200 to 1,800 watts, suitable for smaller kitchens or limited electrical capacity. In contrast, 240V induction stoves can deliver up to 3,700 watts, supporting multiple burners and higher heat output essential for heavy cooking demands.
Understanding 120V vs. 240V Electrical Systems
Induction stoves operating on 120V electrical systems typically provide lower power output, usually around 1,800 to 1,900 watts, which is sufficient for basic cooking tasks but may limit high-heat applications. In contrast, 240V systems deliver higher wattage, often between 3,000 to 3,700 watts, enabling faster heat-up times and more consistent cooking performance ideal for multitasking kitchens. Understanding the electrical infrastructure of your home is crucial when selecting an induction stove, as 240V installations often require dedicated wiring and circuit breakers to accommodate higher power demands safely.
Key Differences Between 120V and 240V Induction Stoves
120V induction stoves typically provide lower wattage, usually up to 1800 watts, suitable for smaller kitchens or portable use, whereas 240V models deliver higher power output, often exceeding 3500 watts, allowing faster heating and supporting larger cooktops. The voltage difference impacts energy efficiency and cooking speed, with 240V units offering more consistent and rapid temperature control due to increased electrical capacity. Installation requirements also vary, as 240V induction stoves need dedicated circuits and compatible wiring, making them ideal for residential or commercial kitchens with heavier cooking demands.
Power Output and Cooking Performance Comparison
Induction stoves operating at 240V provide higher power output, typically ranging between 3,000 to 3,700 watts, enabling faster heating and improved cooking performance. In contrast, 120V induction stoves generally offer lower power output around 1,200 to 1,800 watts, which may limit cooking speed and efficiency for high-heat tasks. The increased voltage of 240V units supports consistent temperature control and quicker response times, critical for precise culinary techniques.
Energy Efficiency: 120V vs. 240V Induction Stoves
240V induction stoves typically offer higher power output and improved energy efficiency compared to 120V models due to reduced current draw and minimized energy loss in electrical resistance. Operating at 240V allows the stove to heat cookware faster and maintain stable temperatures with less electrical strain, optimizing overall performance. Choosing a 240V induction stove can lead to lower energy consumption and enhanced cooking precision, particularly for high-demand culinary tasks.
Installation Requirements and Compatibility
Induction stoves designed for 120V typically require a dedicated 15-20 amp circuit with a standard household outlet, making installation simpler and compatible with most residential kitchens. In contrast, 240V induction stoves demand a dedicated double-pole circuit breaker and specialized wiring, often necessitating professional installation to ensure electrical load capacity and safety compliance. Compatibility depends on existing kitchen wiring; 120V units fit typical single-phase power setups, while 240V models leverage higher voltage for faster heating and greater power output, requiring appropriate infrastructure upgrades.
Safety Considerations for Different Voltages
Induction stoves operating at 240V typically deliver higher power output, enabling faster heating and improved efficiency compared to 120V models, but require dedicated circuits to prevent electrical overloads. Safety considerations include ensuring proper grounding, using circuit breakers rated for the stove's amperage, and avoiding overloading residential wiring which is more common with 120V installations. Compliance with local electrical codes and installation by certified electricians minimizes risks of fire hazards and electrical shocks associated with mismatched voltage supply.
Cost Analysis: Purchase, Installation, and Operation
Induction stoves operating at 240V typically incur higher upfront costs for both purchase and installation due to the need for specialized wiring and circuit breakers. While 120V models are generally less expensive and easier to install, they may consume more energy over time, resulting in higher operational costs. Evaluating the long-term energy efficiency and electricity rates is essential for accurate cost analysis between 120V and 240V induction stove options.
Choosing the Right Voltage for Your Kitchen
Choosing between 120V and 240V for your induction stove depends on your kitchen's electrical capacity and cooking needs. A 240V induction stove provides higher power output, enabling faster heating and better performance for larger cookware. Ensure your kitchen's wiring and circuit breakers can support 240V to maximize efficiency and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions About Induction Stove Voltages
Induction stoves typically operate on either 120V or 240V power supplies, with 240V models providing higher wattage for faster and more efficient cooking. Most residential kitchens in the U.S. requiring rapid heating and higher power consumption opt for 240V induction stoves, which can range from 3,000 to 5,500 watts compared to 1,200 to 1,800 watts for 120V units. For optimal performance, a dedicated 240V circuit is often recommended to meet the stove's power requirements and prevent electrical overload.
120V vs 240V for Induction Stove Power Requirements Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com