Slow juicers use a gentle cold-press method that minimizes oxidation by reducing heat generation and exposure to air, preserving nutrients and enzymes in the juice. High-speed juicers operate with rapid blades that introduce more oxygen, accelerating oxidation and potentially diminishing the juice's freshness and nutritional value. Choosing a slow juicer helps maintain the juice's purity and extends its shelf life compared to high-speed counterparts.
Table of Comparison
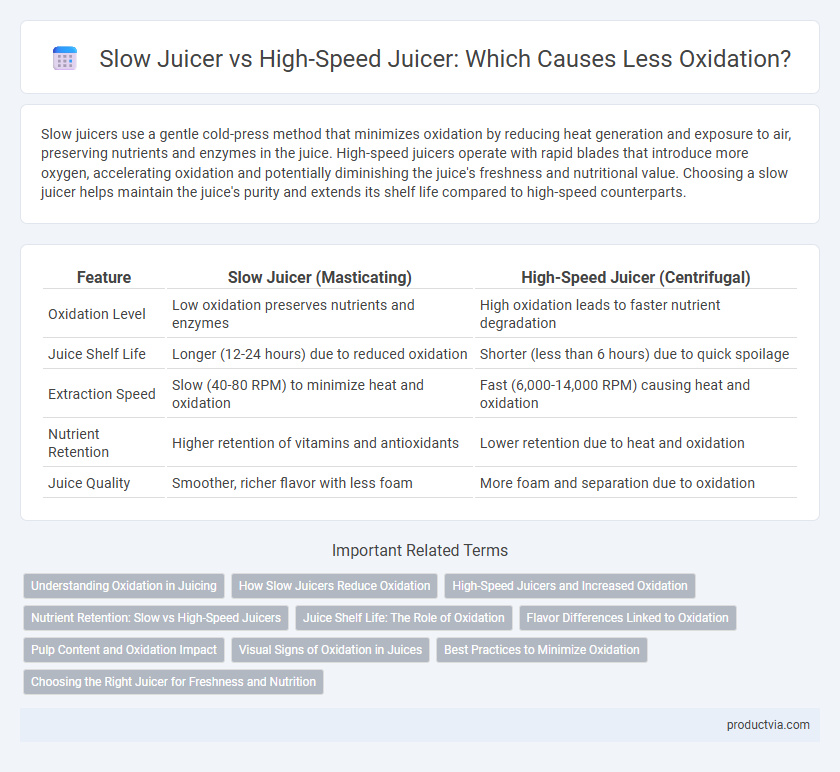
| Feature | Slow Juicer (Masticating) | High-Speed Juicer (Centrifugal) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Level | Low oxidation preserves nutrients and enzymes | High oxidation leads to faster nutrient degradation |
| Juice Shelf Life | Longer (12-24 hours) due to reduced oxidation | Shorter (less than 6 hours) due to quick spoilage |
| Extraction Speed | Slow (40-80 RPM) to minimize heat and oxidation | Fast (6,000-14,000 RPM) causing heat and oxidation |
| Nutrient Retention | Higher retention of vitamins and antioxidants | Lower retention due to heat and oxidation |
| Juice Quality | Smoother, richer flavor with less foam | More foam and separation due to oxidation |
Understanding Oxidation in Juicing
Slow juicers operate at lower RPMs, minimizing oxidation by reducing exposure to heat and air, which better preserves nutrients and antioxidants in fruits and vegetables. High-speed juicers generate more heat and incorporate more air during extraction, accelerating oxidation and potentially degrading sensitive vitamins such as vitamin C. Understanding oxidation's impact on nutrient retention helps in choosing a juicer that balances nutrient preservation with juice extraction speed.
How Slow Juicers Reduce Oxidation
Slow juicers operate at lower RPMs, which significantly reduces heat generation and exposure to oxygen, minimizing oxidation in the juice. This preservation of nutrients and enzymes ensures a fresher taste and longer shelf life compared to high-speed juicers. By gently crushing and pressing fruits and vegetables, slow juicers maintain the juice's natural color and nutritional value.
High-Speed Juicers and Increased Oxidation
High-speed juicers operate at rapid RPMs, which exposes juice to more air, significantly increasing oxidation and reducing nutrient retention. This accelerated oxidation causes faster degradation of vitamins like vitamin C and antioxidants, impacting juice freshness and health benefits. Users seeking longer-lasting nutrient content may find slow juicers preferable due to their lower oxidation rates.
Nutrient Retention: Slow vs High-Speed Juicers
Slow juicers, also known as masticating juicers, operate at low speeds that minimize oxidation, preserving higher levels of vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants in the juice. High-speed juicers, or centrifugal juicers, generate more heat and introduce more air, accelerating nutrient degradation and reducing overall nutritional value. Studies show slow juicers retain up to 30% more vitamin C and other sensitive nutrients compared to high-speed models, making them preferable for maximum nutrient retention.
Juice Shelf Life: The Role of Oxidation
Slow juicers operate at lower RPMs, significantly reducing oxidation and preserving more nutrients, which extends juice shelf life up to 72 hours when refrigerated. High-speed juicers generate heat and incorporate air quickly, accelerating oxidation and nutrient degradation, often limiting juice freshness to less than 24 hours. Choosing a slow juicer minimizes nutrient loss caused by oxidation, maintaining juice quality and flavor for longer periods.
Flavor Differences Linked to Oxidation
Slow juicers operate at low RPMs, minimizing oxidation and preserving the fresh, natural flavor of fruits and vegetables. High-speed juicers generate heat and introduce more air during extraction, accelerating oxidation that can cause a slightly bitter or sour taste. The reduced oxidation in slow juicing maintains vibrant colors and sweeter, more nutrient-rich juice compared to the often harsher flavor profile of high-speed juicing.
Pulp Content and Oxidation Impact
Slow juicers operate at low RPMs, minimizing oxidation and preserving higher nutrient levels and pulp content, which enhances fiber intake and juice freshness. High-speed juicers generate more heat and air exposure, accelerating oxidation that degrades nutrients and often results in less pulp retention. The slower process of masticating juicers ensures a longer shelf life and richer antioxidant presence compared to centrifugal juicers prone to rapid nutrient loss due to oxidation.
Visual Signs of Oxidation in Juices
Slow juicers minimize oxidation by gently pressing fruits and vegetables, preserving the juice's vibrant color and reducing browning. High-speed juicers expose juice to more air and heat, often resulting in rapid color changes, such as dullness or foaming, indicating oxidation. Visual signs like a cloudy appearance or separation are more prominent in high-speed juiced products, signaling faster nutrient degradation.
Best Practices to Minimize Oxidation
Choosing a slow juicer significantly reduces oxidation due to its gentle, masticating extraction method that minimizes exposure to air and heat. To minimize oxidation in high-speed juicers, promptly consume the juice and store it in airtight, dark containers to slow down nutrient degradation. Using fresh produce and cleaning juicer parts immediately after use also helps preserve the juice's freshness and nutrient content.
Choosing the Right Juicer for Freshness and Nutrition
Slow juicers operate at lower RPMs, reducing oxidation and preserving more nutrients and enzymes, which results in fresher, longer-lasting juice. High-speed juicers generate heat and incorporate more air, accelerating oxidation and causing rapid nutrient degradation. Selecting a slow juicer is ideal for maximizing juice freshness, nutrient retention, and flavor quality.
Slow Juicer vs High-Speed Juicer for oxidation Infographic
 productvia.com
productvia.com